Ethylene gas, a natural plant hormone, plays a crucial role in the ripening of fruits and vegetables. Understanding the influence of ethylene and adopting effective management strategies are essential for preserving the freshness and shelf life of your produce. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of ethylene gas, how it affects the ripening process of vegetables, and strategies to separate ethylene-producing and ethylene-sensitive vegetables.
1. What is Ethylene Gas?
Ethylene (C2H4) is a natural plant hormone produced by fruits and vegetables. It acts as a signaling molecule, influencing various physiological processes, including seed germination, flowering, and fruit ripening. Ethylene is responsible for initiating and accelerating the ripening of many fruits and some vegetables.
2. Ethylene’s Influence on Vegetable Ripening
Ethylene gas affects the ripening of vegetables through a process known as ethylene-induced ripening. When exposed to ethylene, vegetables release their own ethylene gas, initiating a series of changes that lead to ripening:
- Color Change: Ethylene triggers the production of pigments responsible for changes in color, such as the transition from green to red in tomatoes.
- Flavor Development: Ethylene stimulates the conversion of starches to sugars, enhancing the sweetness and flavor of fruits and vegetables.
- Softening: Ethylene induces the production of enzymes that break down cell wall components, resulting in softening and texture changes.
- Aroma and Aroma Compounds: Ethylene plays a role in the formation of volatile compounds that contribute to aroma and taste.
https://styledegree.sg/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/ethylene-gas-infographic-styledegree.jpg
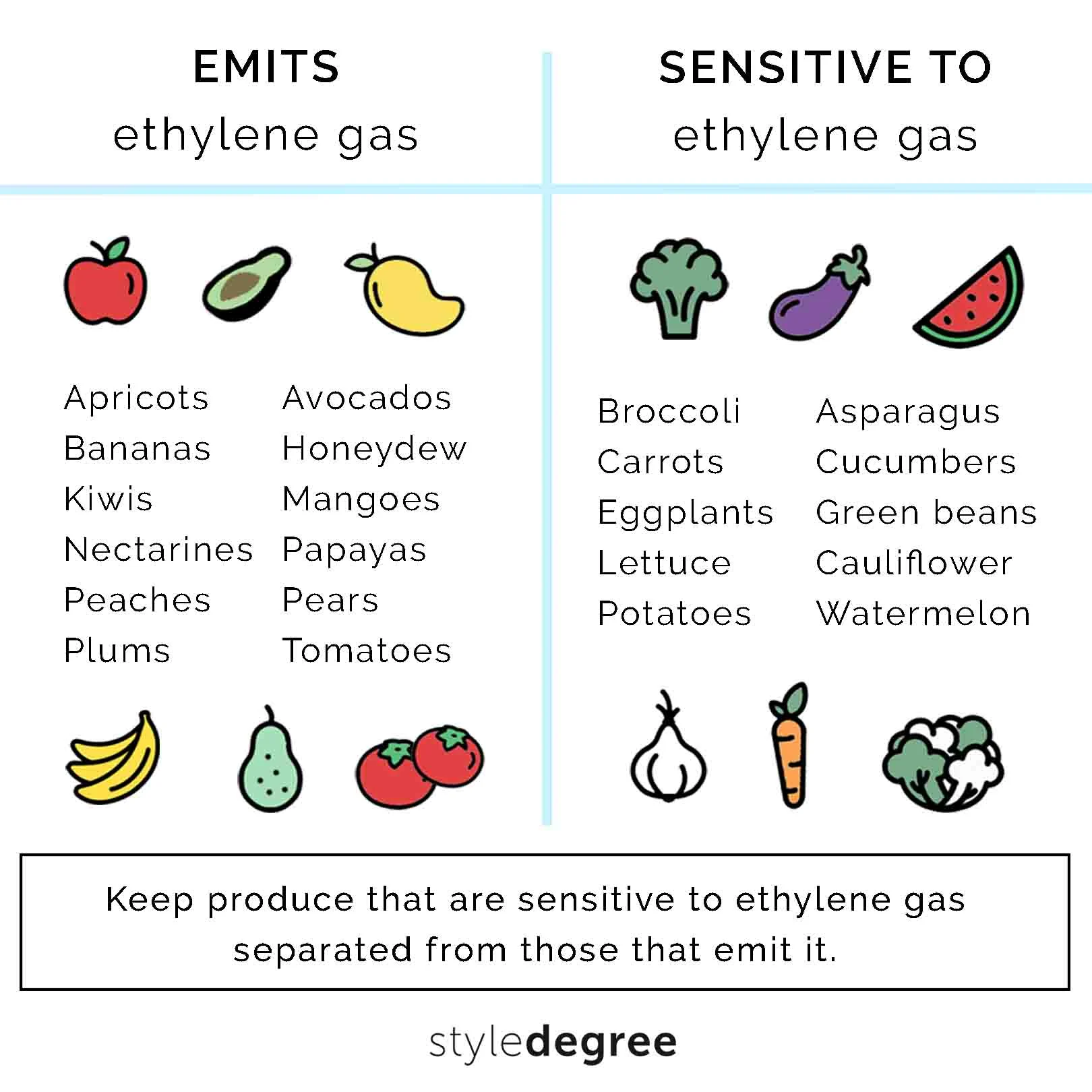
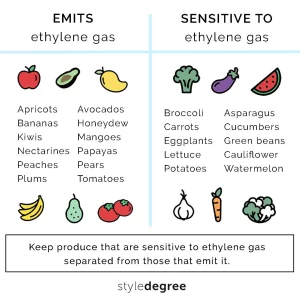
3. Ethylene-Producing Vegetables
Some vegetables are considered ethylene producers and release this gas as they ripen. These include:
- Tomatoes
- Bananas
- Avocados
- Apples
- Peaches
- Pears
- Cantaloupes
- Kiwis
4. Ethylene-Sensitive Vegetables
On the other hand, certain vegetables are ethylene-sensitive, meaning they can be adversely affected by exposure to ethylene gas. Ethylene sensitivity can lead to premature ripening, over-ripening, off-flavors, and textural changes. Examples of ethylene-sensitive vegetables include:
- Leafy Greens (e.g., lettuce, spinach)
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Carrots
- Cucumbers
- Bell Peppers
- Asparagus
- Zucchini
- Green Beans
5. Strategies for Ethylene Gas Management
Effective ethylene gas management is essential to maintain the freshness and quality of your vegetables. Here are strategies to separate ethylene-producing and ethylene-sensitive vegetables:
- Use Ethylene-Blocking Bags or Containers: Specialized ethylene-blocking bags or containers are available for storing ethylene-sensitive vegetables. These products absorb and neutralize ethylene gas, protecting your produce.
- Store Ethylene Producers Separately: Keep ethylene-producing vegetables in a separate section of your refrigerator or storage area. This prevents their gas from affecting nearby ethylene-sensitive items.
- Use Ventilated Storage Drawers: Some refrigerators come equipped with ethylene-blocking or ventilated drawers specifically designed for storing fruits and vegetables. Utilize these drawers to maintain separation.
- Wrap Ethylene Producers: You can wrap ethylene-producing vegetables in plastic wrap or aluminum foil to contain their gas. For example, wrap the stems of bananas or the crown of a bunch of tomatoes.
- Regularly Clean Your Refrigerator: Cleaning your refrigerator regularly helps remove any accumulated ethylene gas. This is particularly important in the crisper drawers where vegetables are stored.
- Monitor Ripeness: Check ethylene-producing vegetables for ripeness regularly and use them promptly. This prevents them from releasing excess ethylene gas.
- Ethylene Filters: Some refrigerators come with ethylene filters that can be replaced to help manage the gas. If your fridge has this feature, be sure to change the filters as recommended.
- Adjust Refrigerator Humidity: Proper humidity control in your refrigerator’s crisper drawers can help maintain the freshness of your vegetables. High humidity is suitable for ethylene-sensitive vegetables, while low humidity is ideal for ethylene producers.
6. Reducing Food Waste with Ethylene Gas Management
Effective ethylene gas management not only preserves the quality of your vegetables but also reduces food waste. By preventing premature ripening and spoilage, you can enjoy your produce for more extended periods, save money, and contribute to sustainable food consumption.

Conclusion
Ethylene gas management is a valuable strategy for preserving the freshness of your vegetables. Understanding which vegetables produce ethylene and which are sensitive to it is the first step in effective management. By implementing these strategies, you can extend the shelf life of your produce, reduce food waste, and continue to enjoy crisp, flavorful vegetables.