Radiology, a medical specialty that utilizes imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases, has been revolutionized by the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The integration of AI in radiology has not only enhanced diagnostic accuracy but also improved workflow efficiency, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. This article delves into the multifaceted role of AI in radiology, highlighting its applications, benefits, and challenges.
The Evolution of Radiology and the Advent of AI
Radiology has come a long way since the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895. Over the years, various imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound have been developed, each contributing significantly to medical diagnostics. However, the sheer volume of imaging data generated by these modalities has posed a significant challenge for radiologists.
Enter Artificial Intelligence. AI, particularly its subset Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), has emerged as a powerful tool to manage and interpret the vast amounts of imaging data. These technologies leverage algorithms that learn from data, enabling them to identify patterns and make predictions with remarkable accuracy.
Applications of AI in Radiology
Image Analysis and Interpretation
One of the primary applications of AI in radiology is image analysis. AI algorithms can be trained to detect abnormalities in medical images, such as tumors, fractures, and lesions. For instance, AI systems have demonstrated proficiency in identifying lung nodules in chest CT scans, often matching or even surpassing human radiologists in accuracy.
Workflow Optimization
AI can streamline radiology workflows by automating routine tasks. For example, AI can prioritize imaging studies based on the likelihood of critical findings, ensuring that urgent cases are reviewed promptly. This not only improves patient care but also reduces the workload on radiologists.
Quantitative Imaging
AI enables quantitative analysis of medical images, providing precise measurements of anatomical structures and pathological findings. This is particularly useful in monitoring disease progression and response to treatment. For instance, AI can measure tumor size and volume in oncology patients, aiding in treatment planning and follow-up.
Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD)
Computer-Aided Diagnosis systems, powered by AI, assist radiologists in interpreting medical images. These systems provide a second opinion, highlighting areas of concern and suggesting possible diagnoses. CAD has been widely used in mammography for breast cancer detection, significantly improving early diagnosis rates.
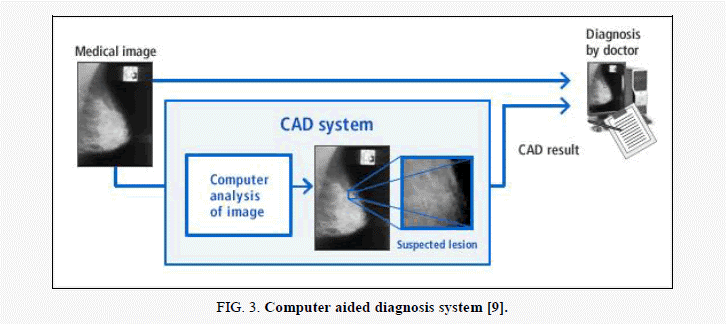
Predictive Analytics
AI can analyze imaging data in conjunction with electronic health records (EHRs) to predict patient outcomes. For example, AI algorithms can forecast the likelihood of disease recurrence or complications, enabling personalized treatment plans. This predictive capability is particularly valuable in chronic diseases such as cardiovascular conditions and oncology.
Benefits of AI in Radiology
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
AI algorithms can detect subtle abnormalities that may be missed by human eyes, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. This is especially crucial in conditions where early detection significantly impacts prognosis, such as cancer.
Increased Efficiency
By automating routine tasks and prioritizing urgent cases, AI allows radiologists to focus on complex cases that require their expertise. This improves overall efficiency and reduces burnout among radiologists.
Consistency and Standardization
AI provides consistent and standardized interpretations of medical images, reducing inter-observer variability. This ensures that patients receive uniform care regardless of the radiologist or institution.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in AI technology may be substantial, the long-term benefits include reduced diagnostic errors, fewer unnecessary tests, and optimized resource utilization. This translates to cost savings for healthcare systems and patients.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its numerous advantages, the integration of AI in radiology is not without challenges.
Data Quality and Quantity
AI algorithms require large amounts of high-quality data for training. Inconsistent or biased data can lead to inaccurate predictions. Ensuring data quality and addressing biases is crucial for the reliability of AI systems.
Interpretability and Transparency
Many AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their conclusions. This lack of interpretability can hinder the acceptance and trust of AI among radiologists and patients.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
The use of AI in healthcare raises regulatory and ethical issues, such as patient privacy, data security, and the potential for algorithmic bias. Regulatory frameworks need to evolve to address these concerns and ensure the safe and ethical use of AI in radiology.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating AI into existing radiology workflows and EHR systems can be challenging. Seamless integration requires significant technical expertise and collaboration between healthcare providers and technology developers.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
AI algorithms need to be continuously updated and retrained to adapt to new data and evolving medical knowledge. This requires ongoing investment in research and development.
The Future of AI in Radiology
The future of AI in radiology is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing adoption in clinical practice. Here are some potential future directions:
Hybrid Models
Combining AI with traditional radiology approaches can enhance diagnostic accuracy and provide comprehensive insights. Hybrid models that integrate imaging data with clinical and genomic information hold great potential for personalized medicine.
Tele-radiology
AI can facilitate tele-radiology by enabling remote interpretation of medical images. This is particularly valuable in underserved areas with limited access to radiology expertise.
AI-Driven Research
AI can accelerate medical research by analyzing vast datasets to identify new disease patterns, biomarkers, and treatment targets. This can lead to the development of innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Education and Training
AI can be used as an educational tool to train radiologists, providing real-time feedback and enhancing their diagnostic skills. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies, combined with AI, can create immersive training experiences.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in radiology represents a paradigm shift in medical imaging, offering numerous benefits in terms of diagnostic accuracy, efficiency, and patient care. However, realizing the full potential of AI requires addressing challenges related to data quality, interpretability, regulatory considerations, and integration with existing systems. As technology continues to evolve, AI is poised to play an increasingly central role in radiology, transforming the way we diagnose and treat diseases and ultimately improving patient outcomes.