Introduction
I’m Dr. Amelia Moore, a veterinarian with over 15 years of experience working in international animal health. Throughout my career, I’ve witnessed firsthand the global trade in live animals, and the concerning realities that often lie beneath the surface. This article delves into the risks associated with animal transport, aiming to raise awareness among policymakers, public health officials, and animal welfare activists.
The Scope of Animal Transport
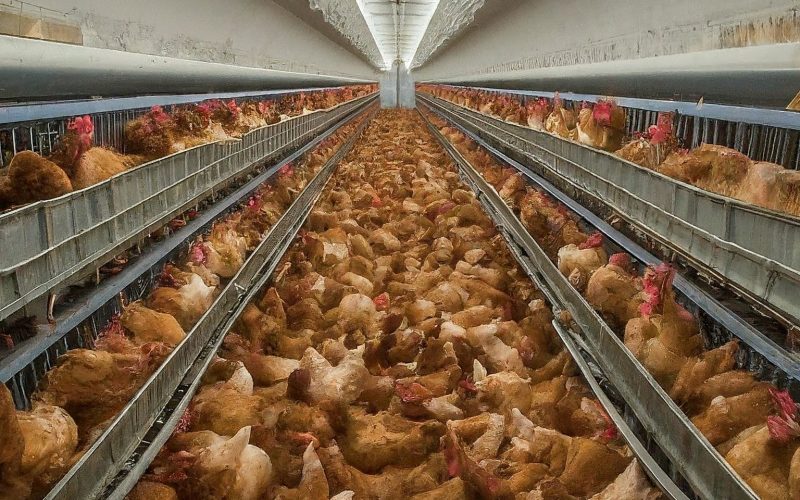
The global trade in live animals is a multi-billion dollar industry, encompassing farm animals, companion animals, and wildlife. Millions are transported across continents each year, destined for slaughterhouses, breeding facilities, zoos, or the pet trade. While regulations exist, ensuring animal welfare and preventing the spread of disease during transport remains a significant challenge.
Risks and Repercussions
Animal Welfare Concerns: Animals endure long journeys crammed into cramped crates with limited access to food, water, and proper ventilation. This can lead to stress, injuries, dehydration, and even death.
Disease Transmission: The close proximity of stressed and potentially infected animals during transport creates a breeding ground for disease outbreaks. Diseases like foot-and-mouth disease in cattle and African swine fever in pigs can have devastating consequences for local agriculture.
Public Health Threats: Zoonotic diseases, those transmissible from animals to humans, pose a serious public health risk. The emergence of diseases like avian influenza and Nipah virus are linked to the global trade in live animals.
Environmental Impact: The transportation of animals by air and land contributes significantly to carbon emissions, further accelerating climate change.

A Look at the Numbers (Informative Table)
| Risk | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Welfare | Stress, injuries, dehydration, and death during transport. | Compromises animal well-being and can result in lower quality meat products. |
| Disease Transmission | Outbreaks of foot-and-mouth disease and African swine fever. | Devastates local agriculture industries, leading to economic losses. |
| Public Health Threats | Emergence of zoonotic diseases like avian influenza and Nipah virus. | Poses a serious risk to public health, potentially leading to pandemics. |
| Environmental Impact | Carbon emissions from air and land transport of animals. | Contributes to climate change and environmental degradation. |
Seeking Solutions: A Call to Action
The current practices surrounding animal transport are unsustainable and pose significant risks to animal welfare, public health, and the environment. Here are some solutions to consider:
- Strengthening regulations: Implementing stricter regulations on animal transport conditions, journey lengths, and rest periods.
- Promoting alternative methods: Exploring alternative methods like the transport of breeding stock or animal products instead of live animals.
- Investing in technology: Utilizing advancements in technology like on-board monitoring systems to ensure animal welfare during transport.
- Raising Public Awareness: Educating policymakers and the public about the hidden dangers of animal transport to generate support for reform.
Conclusion
The global trade in live animals is complex, but the need for change is undeniable. By working together, policymakers, public health officials, and animal welfare activists can implement solutions that prioritize animal well-being, public health, and environmental sustainability. We must move beyond a system that operates beyond borders and beyond control, towards practices that treat animals with respect and prioritize the safety of our planet and its inhabitants.