I am happy to help you write an article about chickenpox, covering the symptoms, causes, and prevention of this viral infection. Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus that primarily affects children, but can also affect adults who have not had the infection before.
Here is a 600-word article that will provide readers with a comprehensive overview of chickenpox:
What You Need to Know about Chickenpox: Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention
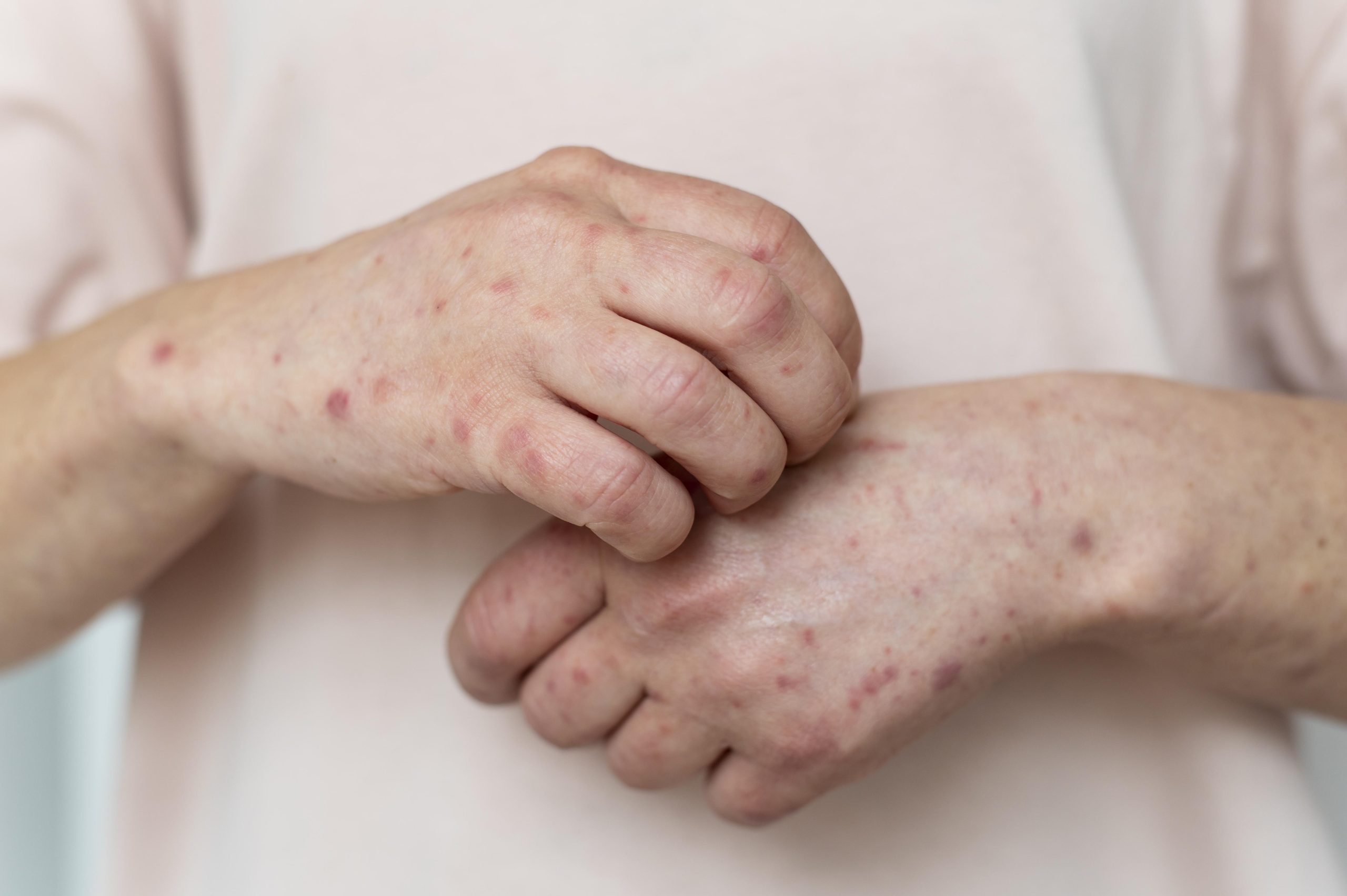
Chickenpox is a viral infection that causes an itchy rash and red spots all over the body. It is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person. Here is what you need to know about chickenpox, including its symptoms, causes, and prevention.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Chickenpox typically starts with a fever, headache, and loss of appetite, followed by the appearance of a rash that spreads all over the body. The rash consists of small, red, itchy spots that turn into blisters filled with fluid. The blisters then break open, forming crusts that eventually fall off. Other symptoms may include a cough, sore throat, and fatigue.
In most cases, chickenpox is a mild illness that lasts about a week or two. However, it can be more severe in infants, adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Causes of Chickenpox
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which spreads from person to person through direct contact or by breathing in droplets from an infected person’s cough or sneeze. The virus can also spread through contact with objects or surfaces contaminated with the virus.
Once a person has been infected with the virus, it can remain dormant in the body and reactivate later in life, causing a painful condition called shingles.
Prevention of Chickenpox
The best way to prevent chickenpox is to get vaccinated. The chickenpox vaccine is safe and effective, and it can prevent the disease or make the symptoms milder if you do get infected. The vaccine is recommended for all children, and adults who have not had chickenpox should also consider getting vaccinated.
If you or your child has not been vaccinated and has been exposed to someone with chickenpox, you may be able to prevent infection by getting a shot of the chickenpox vaccine within 72 hours of exposure. This is known as post-exposure prophylaxis, and it can help prevent or reduce the severity of the infection.
It is also important to practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of chickenpox. This includes washing your hands frequently, avoiding close contact with people who are infected, and covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.
Treatment of Chickenpox
There is no cure for chickenpox, but there are several ways to relieve the symptoms and speed up the healing process. The most effective way to treat chickenpox is to get plenty of rest and stay hydrated. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen