The Climate Crisis in Europe has reached unprecedented levels, characterized by extreme temperatures and prolonged heatwaves. As global warming intensifies, the continent faces dire consequences, including severe health risks and environmental guide degradation. Let’s delve into the complexities of this issue and explore potential solutions.
Current Scenario
Europe is experiencing record-breaking temperatures, with heatwaves becoming more frequent and intense. The soaring mercury levels pose significant challenges to both human health and the ecosystem. From heat-related illnesses to disruptions in agriculture, the impacts of sweltering heat are profound and far-reaching.
Causes of Climate Crisis
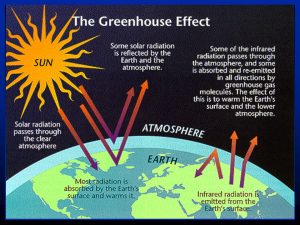
The primary drivers of the Climate Crisis are human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Additionally, widespread deforestation contributes to the imbalance in atmospheric carbon levels, exacerbating global warming.

Consequences of Sweltering Heat
The relentless heat poses numerous risks, including heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and dehydration among vulnerable populations. Furthermore, agricultural sectors face crop failures and water shortages, leading to food insecurity and economic losses.
Mitigation Strategies
To combat the Climate Crisis, innovative solutions are imperative. Embracing renewable energy sources and implementing sustainable agricultural practices can significantly reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Government Initiatives
Governments across Europe are implementing ambitious climate policies and collaborating on international platforms to address the Climate Crisis collectively. Through regulatory measures and investment in clean energy, they aim to curb greenhouse gas emissions and foster sustainable development.
Community Actions
Local communities play a crucial role in climate resilience, implementing adaptation measures and advocating for environmental stewardship. Grassroots movements and community-based initiatives are driving change at the grassroots level, promoting sustainable lifestyles and conservation efforts.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements, such as AI-driven climate modeling and climate-friendly transportation solutions, offer promising avenues for mitigating the Climate Crisis. Leveraging innovation and research can accelerate the transition towards a carbon-neutral future.
Economic Impacts
The Climate Crisis carries significant economic ramifications, with the costs of inaction far outweighing the investments in climate resilience. Embracing green technologies and transitioning to a circular economy present opportunity for sustainable growth and job creation.
Adaptation Challenges
Adapting to the changing climate presents formidable challenges, particularly for vulnerable populations and urban areas susceptible to the urban heat island effect. Addressing inequities and implementing equitable adaptation measures are crucial for building climate resilience.
Educational Campaigns
Raising public awareness and integrating climate education into school curricula are essential components of mitigating the Climate Crisis. Educational campaigns empower individuals to make informed decisions and take collective action towards environmental sustainability.
Global Cooperation
The Paris Agreement serves as a cornerstone for global cooperation in combating climate change, with nations committing to ambitious targets for emissions reduction and climate resilience. Strengthening international partnerships and cooperation is vital for addressing this global challenge effectively.
Future Outlook
Despite the daunting challenges posed by the Climate Crisis, there is cause for optimism. By embracing sustainable practices, fostering innovation, and prioritizing global cooperation, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and build a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
What are the primary causes of the Climate Crisis in Europe?
The Climate Crisis in Europe is primarily driven by human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions and global warming.
How do heatwaves impact agriculture in Europe?
Heatwaves disrupt agricultural activities by causing crop failures, water shortages, and decreased yields. This not only affects food production but also leads to economic losses for farmers and agricultural industries.
What are some government initiatives to combat the Climate Crisis in Europe? Governments in Europe are implementing various climate policies, such as carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable energy incentives, and regulations to reduce emissions from industries and transportation sectors.
How can communities contribute to climate resilience?
Communities can contribute to climate resilience by implementing local adaptation measures, promoting sustainable lifestyles, and advocating for environmental conservation through grassroots movements and community-based initiatives.
What role do technological innovations play in addressing the Climate Crisis? Technological innovations, such as AI-driven climate modeling and climate-friendly transportation solutions, offer promising avenues for mitigating the Climate Crisis by reducing carbon emissions and fostering sustainable practices.
Why is global cooperation essential in combating climate change?
Global cooperation is essential in combating climate change because it requires coordinated efforts from nations worldwide to address this global challenge effectively. Initiatives like the Paris Agreement facilitate collaboration and collective action towards climate resilience.
Conclusion
The Climate Crisis gripping Europe with its sweltering heat spells deadly consequences demands urgent action and collective responsibility. As we navigate through the challenges posed by rising temperatures and extreme weather events, it’s imperative to prioritize sustainability, resilience, and innovation. By implementing comprehensive mitigation strategies, embracing renewable energy solutions, and fostering global cooperation, we can chart a path towards a more sustainable future. Governments, communities, and individuals must work together to address the root causes of the Climate Crisis and mitigate its impacts on both people and the planet.










