Introduction
The global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus, COVID-19, has spurred extensive research into its effects on various aspects of health. Among the population segments vulnerable to severe outcomes of COVID-19, individuals with underlying health conditions such as diabetes have been of particular concern. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the potential connection between COVID-19 and diabetes, exploring the scientific evidence, implications, and preventive measures. All You Need To Know About (arms And Legs Tingling)
Understanding COVID-19 and Diabetes
1. COVID-19: A Brief Overview
COVID-19, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, primarily targets the respiratory system and can lead to severe respiratory distress and other complications. Since its emergence in late 2019, the virus has rapidly spread worldwide, prompting unprecedented public health responses.
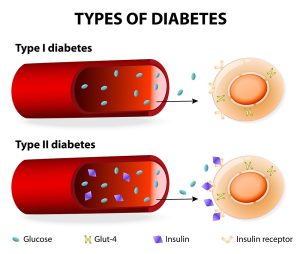
2. Diabetes: An Overview
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective utilization of insulin by the body. Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity.
Examining the Potential Connection
1. Impact on Diabetes Patients
Studies have indicated that individuals with diabetes, particularly those with poorly controlled blood sugar levels, may face an increased risk of severe COVID-19 complications, including respiratory failure and death. The underlying immune dysfunction and inflammation observed in diabetes patients could exacerbate the body’s response to viral infections like COVID-19.
2. Mechanisms of Interaction
Several potential mechanisms may underlie the interaction between COVID-19 and diabetes. These include:
- ACE2 Receptor Expression: The SARS-CoV-2 virus enters human cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, which is highly expressed in tissues relevant to both diabetes and COVID-19 complications.
- Immune Dysregulation: Diabetes is associated with impaired immune function, which may compromise the body’s ability to mount an effective defense against viral infections.
- Inflammatory Response: COVID-19 can trigger a systemic inflammatory response, known as a cytokine storm, which may be more pronounced in individuals with diabetes, leading to further complications.
Clinical Implications and Recommendations
1. Management Strategies
For individuals with diabetes, effective management of blood sugar levels and adherence to prescribed medications are crucial for reducing the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes. This includes:
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels can help diabetes patients maintain optimal control and detect any deviations promptly.
- Medication Adherence: Strict adherence to prescribed medications, including insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents, is essential to prevent fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can help improve overall metabolic health and immune function.
2. Vaccination
Vaccination against COVID-19 is strongly recommended for individuals with diabetes, as it can significantly reduce the risk of severe illness and complications. Vaccines have been shown to be safe and effective in this population, offering protection against severe outcomes of COVID-19.
COVID-19 and Diabetes
| Aspect | COVID-19 | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Factors | Advanced age, comorbidities | Obesity, sedentary lifestyle |
| Mechanisms of Interaction | ACE2 receptor expression, immune dysregulation | Insulin resistance, inflammation |
| Management Strategies | Vaccination, respiratory support | Blood sugar monitoring, medication adherence |
| Clinical Implications | Severe respiratory distress, cytokine storm | Hyperglycemia, cardiovascular complications |
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the exact nature of the connection between COVID-19 and diabetes continues to be elucidated through ongoing research, there is compelling evidence to suggest that individuals with diabetes may face an elevated risk of severe COVID-19 complications. By understanding the mechanisms of interaction and implementing appropriate management strategies, including vaccination and lifestyle modifications, individuals with diabetes can mitigate their risk and protect their health during the ongoing pandemic.