Introduction:
Meet Dr. Emily Parker, a distinguished child psychologist with over 20 years of experience specializing in early childhood development. Dr. Parker has dedicated her career to understanding the intricacies of children’s learning environments and how they impact cognitive, social, and emotional growth. In this article, she shares her expertise on designing enriching spaces for learning birth to age eight laying the foundation for lifelong learning.
Understanding learning birth to age eight

During the first two years of life, children undergo rapid brain development, forming crucial neural connections that shape their future learning abilities. Dr. Parker emphasizes the significance of sensory stimulation, responsive caregiving, and safe exploration during this critical period.
Creating Stimulating Sensory Experiences
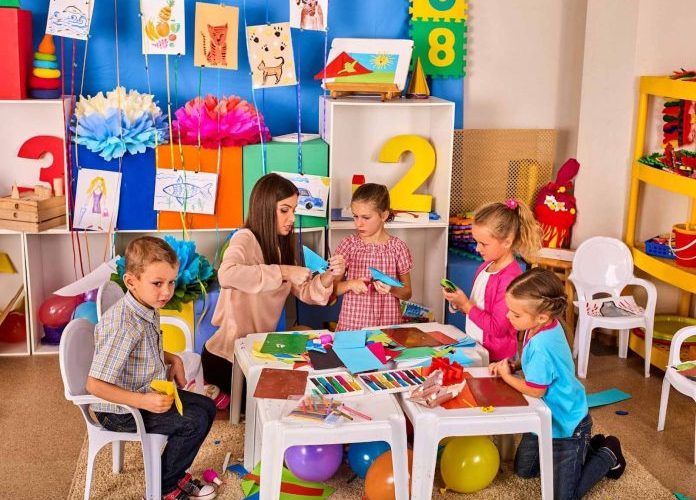
As toddlers transition into preschoolers, their curiosity blossoms, and they become increasingly interested in exploring their surroundings. Dr. Parker advocates for designing environments rich in sensory experiences, incorporating elements such as textured surfaces, vibrant colors, and interactive materials to engage young learners’ senses.
Fostering Social Interaction
At ages 4-6, children thrive in environments that promote social interaction and cooperative play. Dr. Parker highlights the importance of arranging spaces to encourage peer collaboration, communication, and conflict resolution. Designing inclusive play areas and group activities cultivates essential social skills and empathy.
Encouraging Independent Exploration

As children enter the primary school years, they develop a greater sense of independence and autonomy. Dr. Parker advises on creating learning environments that empower children to take initiative, make choices, and pursue their interests autonomously. Providing a variety of hands-on activities and resources fosters a sense of agency and self-confidence.
Expert Insight: Dr. Emily Parker
Investing in early learning environments tailored to children’s developmental needs lays a solid foundation for future academic success and overall well-being. By understanding the unique characteristics of each age group, educators and caregivers can create nurturing spaces that inspire curiosity, creativity, and lifelong love for learning.
Key Points Summary:
| Age Group | Essential Elements |
|---|---|
| 0-2 years | Sensory stimulation |
| Responsive caregiving | |
| Safe exploration | |
| 2-4 years | Textured surfaces |
| Vibrant colors | |
| Interactive materials | |
| 4-6 years | Social interaction |
| Cooperative play | |
| Inclusive environments | |
| 6-8 years | Independent exploration |
| Hands-on activities | |
| Choice-based learning |
Comparative Table: Age-Specific Needs
| Age Group | Key Needs |
|---|---|
| 0-2 years | Sensory Stimulation |
| Responsive Caregiving | |
| Safety & Security | |
| 2-4 years | Exploration & Curiosity |
| Hands-on Learning | |
| Social Interaction | |
| 4-6 years | Cooperative Play |
| Communication Skills | |
| Emotional Regulation | |
| 6-8 years | Independence & Autonomy |
| Critical Thinking | |
| Problem-Solving Skills |
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Dr. Emily Parker’s insights shed light on the crucial elements of designing learning environments tailored to children aged 0-8. By understanding the unique developmental stages and needs of each age group, educators and caregivers can create enriching spaces that foster holistic growth and ignite a lifelong passion for learning. Remember, the building blocks of learning begin in early childhood, laying the groundwork for future success and fulfillment.