Introduction
Understanding ear congestion is crucial for anyone who has experienced the discomfort of blocked ears. Ear congestion, often described as a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears, can be caused by various factors. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the reasons behind ear congestion and explore effective ways to alleviate this discomfort. Explore More About (Teeth And Bones Health)
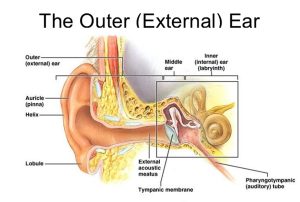
Anatomy of the Ear
To comprehend why ear congestion occurs, it’s essential to grasp the basic anatomy of the ear. The ear consists of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
Outer Ear
The outer ear includes the visible portion known as the pinna or auricle, which collects sound waves and channels them into the ear canal. The ear canal, lined with specialized skin cells, leads to the eardrum (tympanic membrane) in the middle ear.
Middle Ear
Behind the eardrum lies the middle ear, a small air-filled chamber containing three tiny bones called the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The middle ear is also connected to the back of the nose and throat by the Eustachian tube, which helps maintain equal air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
Inner Ear
The inner ear comprises the cochlea, responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals sent to the brain, and the semicircular canals, which contribute to balance and spatial orientation.
Causes of Ear Congestion
Now that we have a basic understanding of ear anatomy, let’s explore the various factors that can lead to ear congestion:
1. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tube plays a crucial role in regulating pressure in the middle ear. Dysfunction of this tube, often due to allergies, sinus infections, or changes in altitude, can result in a feeling of ear fullness or blockage.
2. Ear Infections
Infections of the middle ear, known as otitis media, can cause inflammation and fluid buildup behind the eardrum, leading to ear congestion and discomfort. These infections are common, particularly in children.
3. Wax Buildup
Accumulation of earwax (cerumen) in the ear canal can obstruct sound waves and cause a sensation of fullness or pressure in the ears. Using cotton swabs or other objects to clean the ears can push wax deeper, exacerbating the problem.
4. Allergic Reactions
Allergies to environmental triggers such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander can cause swelling and congestion in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, leading to ear congestion.
5. Barotrauma
Rapid changes in air pressure, such as during air travel, scuba diving, or driving through mountains, can result in barotrauma, causing ear discomfort and congestion.

Symptoms of Ear Congestion
Identifying the symptoms of ear congestion is crucial for proper management and relief. Common symptoms include:
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears
- Muffled hearing
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears)
- Difficulty balancing
Treatment and Remedies
1. Nasal Decongestants
Over-the-counter nasal decongestant sprays or oral medications can help relieve congestion by reducing swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. However, prolonged use of nasal decongestants can lead to rebound congestion and should be used with caution.
2. Steam Inhalation
Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water or using a facial steamer can help loosen mucus and alleviate congestion in the nasal passages and ears.
3. Ear Irrigation
For stubborn earwax buildup, irrigation with warm water or saline solution can help soften and remove excess wax. It’s essential to use caution and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
4. Allergy Management
Managing allergies with antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, or allergy shots can help reduce inflammation and congestion in the ears and nasal passages.
5. Ear Tubes
In cases of chronic Eustachian tube dysfunction or recurrent ear infections, a surgical procedure to insert small tubes into the eardrums can help equalize pressure and improve ventilation in the middle ear.

Treatment Options
| Treatment | Description |
|---|---|
| Nasal Decongestants | Over-the-counter sprays or oral medications to reduce swelling in nasal passages. |
| Steam Inhalation | Inhaling steam to loosen mucus and alleviate congestion. |
| Ear Irrigation | Flushing the ear canal with warm water or saline to remove excess wax. |
| Allergy Management | Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, or allergy shots to reduce inflammation. |
| Ear Tubes | Surgical insertion of tubes into the eardrums to equalize pressure in the middle ear. |
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild ear congestion can often be managed at home with conservative measures, certain situations warrant medical evaluation. It’s advisable to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe ear pain
- Prolonged or worsening ear congestion
- Fever
- Drainage from the ear
- Sudden hearing loss
Conclusion
Ear congestion can be a bothersome symptom, but understanding its underlying causes and appropriate management strategies can provide relief. By addressing factors such as Eustachian tube dysfunction, ear infections, wax buildup, allergies, and barotrauma, you can effectively alleviate ear congestion and restore comfort. If symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a healthcare professional for personalized evaluation and treatment.