Introduction
Eye twitching, although often harmless, can be a bothersome and persistent issue for many individuals. Understanding the causes behind this involuntary movement of the eyelid muscle, known as myokymia, is essential in effectively managing and preventing its occurrence. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various factors that contribute to eye twitching and provide practical tips on how to alleviate and prevent this common phenomenon. Explore More About (Knees Arthritis Shots)
Understanding Eye Twitching
What is Eye Twitching?
Eye twitching, medically referred to as blepharospasm, is the repetitive, involuntary spasm of the eyelid muscles. It typically manifests as rapid, uncontrollable movements of the upper or lower eyelid, causing a fluttering sensation. While occasional eye twitching is common and usually harmless, persistent or chronic twitching may indicate an underlying issue that requires attention.
Types of Eye Twitching
There are two primary types of twitching:
1. Benign Essential Blepharospasm (BEB):
This type of twitching is considered benign and typically occurs without any underlying neurological condition. It often affects both eyes and can be triggered or exacerbated by stress, fatigue, caffeine, or eye strain.
2. Hemifacial Spasm:
Hemifacial spasm involves involuntary contractions of one side of the face, including the eyelid, cheek, and mouth muscles. Unlike BEB, hemifacial spasm may be associated with underlying neurological conditions such as a compression of the facial nerve by a blood vessel.

Common Causes of Eye Twitching
Understanding the potential triggers of twitching is crucial for effectively managing and preventing its recurrence. While the exact cause may vary from person to person, several common factors can contribute to this phenomenon:
1. Stress and Fatigue:
High levels of stress and fatigue can overstimulate the nervous system, leading to muscle spasms and twitching, including those of the eyelids.
2. Caffeine and Alcohol Consumption:
Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol can disrupt the body’s natural balance, resulting in heightened nervous system activity and increased likelihood of twitching.
3. Eye Strain:
Prolonged periods of screen time, reading, or other activities that require intense focus can strain the eye muscles, triggering twitching and discomfort.
4. Dry Eyes:
Insufficient lubrication of the eyes, often due to environmental factors or certain medications, can cause irritation and twitching of the eyelids.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies:
Inadequate intake of certain nutrients, such as magnesium or potassium, may contribute to muscle spasms and twitching, including those affecting the eyelids.
6. Lack of Sleep:
Inadequate sleep can impair the body’s ability to function optimally, increasing susceptibility to various involuntary muscle movements, including twitching.
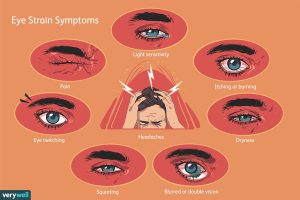
How to Stop Eye Twitching
While occasional eye twitching may resolve on its own, persistent or bothersome twitching may require intervention to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. Here are some effective strategies for managing and stopping eye twitching:
1. Get Adequate Rest:
Prioritize quality sleep to allow your body and eyes to rest and recover fully. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night to promote overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of twitching.
2. Reduce Stress Levels:
Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to lower stress levels and promote relaxation. Managing stress effectively can help prevent twitching triggered by heightened nervous system activity.
3. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake:
Cut back on caffeine and alcohol consumption, especially close to bedtime, to minimize their stimulant effects on the nervous system. Opt for caffeine-free beverages and limit alcohol intake to promote better sleep quality and reduce the risk of twitching.
4. Take Regular Breaks from Screens:
Follow the 20-20-20 rule when using digital devices: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away. This practice helps reduce eye strain and fatigue associated with prolonged screen time, reducing the likelihood of twitching.
5. Use Warm Compresses:
Apply a warm compress to the affected eye for a few minutes several times a day to help relax the muscles and alleviate twitching. The warmth can also improve circulation and relieve tension in the eyelids.
6. Stay Hydrated:
Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate dry eye symptoms and contribute to eye . Aim to consume at least 8 glasses of water daily to maintain optimal hydration levels.

7. Consider Nutritional Supplements:
Consult with a healthcare professional about incorporating magnesium or potassium supplements into your diet, especially if you suspect a deficiency may be contributing to twitching. These minerals play essential roles in muscle function and may help reduce twitching frequency.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of twitching resolve on their own or with simple lifestyle modifications, persistent or severe twitching may warrant medical evaluation. Consult an eye care professional if you experience any of the following:
- Twitching lasting longer than a few weeks
- Twitching accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as eye pain, redness, or vision changes
- Twitching that significantly interferes with daily activities or quality of life
Your eye care provider can perform a thorough evaluation to identify any underlying causes of your twitching and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Eye Twitching vs. Hemifacial Spasm
| Aspect | Eye Twitching | Hemifacial Spasm |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Involuntary eyelid spasms | Involuntary contractions of one side of the face |
| Duration | Usually brief and intermittent | Continuous or persistent |
| Underlying Cause | Stress, fatigue, caffeine, dry eyes, nutritional deficiency | Compression of facial nerve by a blood vessel |
| Treatment | Lifestyle modifications, stress management, warm compresses | Medications, botulinum toxin injections, surgical intervention |
| Prognosis | Generally benign and self-limiting | May require ongoing management and treatment |
Conclusion
Eye twitching, while often benign, can be a source of annoyance and discomfort for many individuals. By understanding the potential causes and triggers of twitching, as well as implementing practical strategies for prevention and management, you can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve overall eye health. Remember to prioritize rest, stress management, and healthy habits to keep your eyes functioning optimally and twitch-free.
Incorporate the tips outlined in this guide into your daily routine to minimize the occurrence of twitching and promote lasting eye comfort and wellness.