Introduction
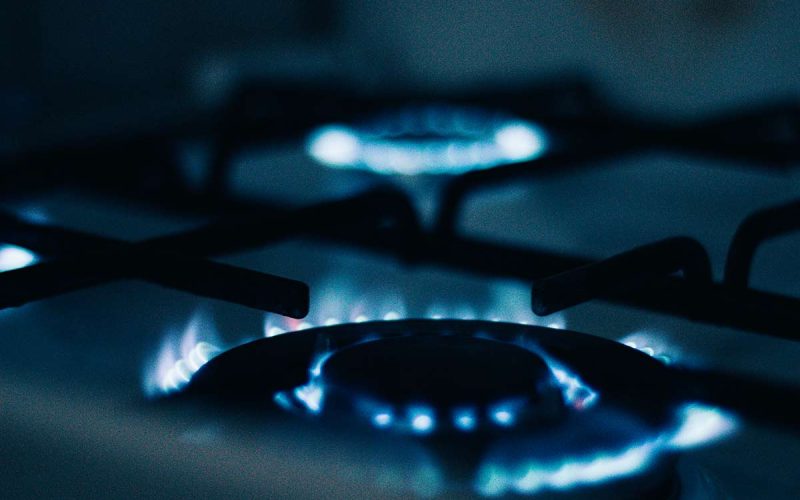
Gas stoves have long been a staple in kitchens worldwide, offering convenience and efficiency in cooking. However, amidst their practicality lies a hidden threat: gas stove pollution. This article delves into the adverse health effects of gas stove pollution and provides practical steps to mitigate its impact, safeguarding both individuals and the environment.
Health Risks Associated with Gas Stove Pollution
Gas stoves emit a variety of pollutants during use, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde, and particulate matter. Prolonged exposure to these substances can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and even neurological disorders. Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable.
Common Pollutants Released by Gas Stoves
Carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas, poses a severe health risk by interfering with oxygen transport in the body. Nitrogen dioxide, produced through incomplete combustion, irritates the respiratory system and exacerbates asthma symptoms. Formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, is released from gas stoves during cooking and poses long-term health hazards.

Symptoms of Gas Stove Pollution
Exposure to gas stove pollutants can manifest in various symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, and fatigue. Chronic exposure may lead to more severe health complications, such as respiratory infections, heart disease, and neurological disorders. Recognizing these signs is crucial for early intervention and prevention. Explore More About (Monkeypox Solution)

Easy Steps to Reduce Gas Stove Pollution
- Switching to Electric Appliances: Transitioning to electric stoves eliminates direct combustion and significantly reduces indoor air pollution.
- Proper Ventilation Techniques: Installing exhaust hoods and opening windows during cooking promote airflow and minimize pollutant buildup.
- Regular Maintenance of Gas Stoves: Cleaning burners, checking for gas leaks, and servicing appliances annually ensure efficient and safe operation.
- Cooking Habits for Minimizing Pollution: Using lids on pots and pans, cooking at lower temperatures, and avoiding charred or burnt food reduce pollutant emissions.
- Investing in High-Quality Cookware: Opting for non-toxic materials like stainless steel or cast iron reduces the release of harmful chemicals during cooking.
| Factor | Gas Stoves | Electric Cooktops | Induction Cooktops |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emissions | Emit pollutants like CO and NO2 | Produce no emissions | Produce no emissions |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Control | Good | Good | Excellent |
| Cooking Speed | Fast | Moderate | Fast |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven | Even | Even |
| Safety | Risk of gas leaks, open flame | No risk of gas leaks, no open flame | No risk of gas leaks, no open flame |
| Installation | Requires gas line | Requires electrical connection | Requires electrical connection |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and inspection | Easy to clean, no special maintenance | Easy to clean, no special maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Contributes to indoor air pollution | Minimal impact | Minimal impact |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate | High |
Conclusion
In conclusion, combating gas stove pollution is essential for protecting both human health and the environment. By adopting simple yet effective measures such as switching to electric appliances, improving ventilation, and practicing mindful cooking habits, individuals can minimize their exposure to harmful pollutants and create safer living environments for themselves and future generations.