Hot temperatures can have a significant impact on our energy levels, often leading to a condition known as heat exhaustion. Understanding the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon can help shed light on why hot weather zaps our energy.
- Excessive sweating: In hot weather, our bodies produce more sweat as a mechanism to cool down. Sweating is our natural way of dissipating heat. However, excessive sweating can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, both of which can contribute to fatigue and a lack of energy.
- Dehydration: High temperatures, coupled with sweating, can cause a rapid loss of fluids from our bodies. Dehydration occurs when the amount of water leaving our bodies exceeds the amount we take in. Even mild dehydration can lead to feelings of fatigue, weakness, and a decrease in cognitive function.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Sweating not only causes fluid loss but also results in the depletion of essential electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These electrolytes are crucial for proper muscle function, nerve transmission, and overall energy production. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and fatigue.
- Increased metabolic demand: Hot temperatures place an increased metabolic demand on our bodies. Our metabolism works harder to produce energy for various functions, including maintaining an optimal body temperature. This heightened metabolic activity can contribute to feelings of exhaustion and tiredness.
- Blood vessel dilation: When exposed to heat, our blood vessels dilate or expand in order to facilitate heat dissipation through the skin. This redirection of blood flow from internal organs to the skin’s surface can place additional stress on the cardiovascular system, requiring the heart to work harder to maintain adequate blood flow. This increased cardiovascular strain can result in fatigue.
- Disrupted sleep patterns: Hot weather can disrupt our sleep patterns, leading to inadequate rest. Trying to sleep in a hot and uncomfortable environment can make it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. Poor quality sleep can leave us feeling tired and drained during the day.
To prevent or alleviate the effects of heat exhaustion on your energy levels, it is important to take certain measures. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, especially in hot weather or when engaging in physical activities. Try to avoid excessive exposure to heat by seeking shade, wearing lightweight and breathable clothing, and using fans or air conditioning when available. Resting in a cool environment and ensuring adequate sleep can also help combat fatigue caused by hot temperatures.
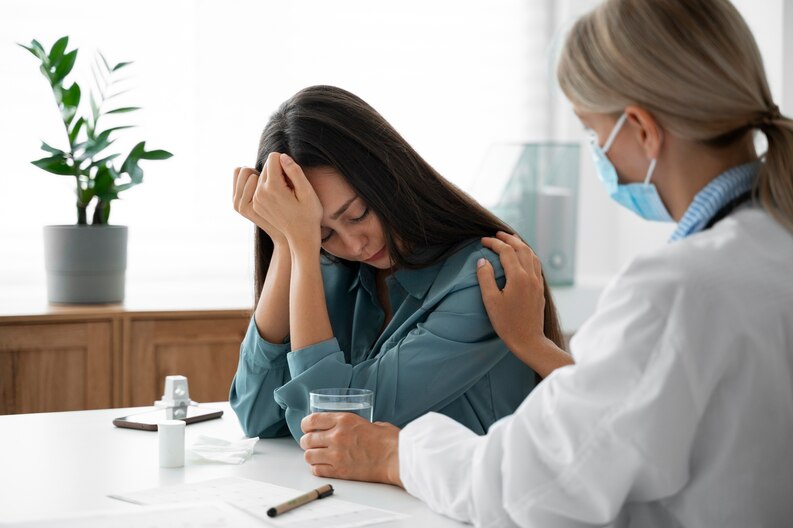
If you or someone you know experiences severe symptoms of heat exhaustion, such as rapid heartbeat, dizziness, confusion, or fainting, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention as it may be indicative of a heatstroke, a more severe heat-related condition.