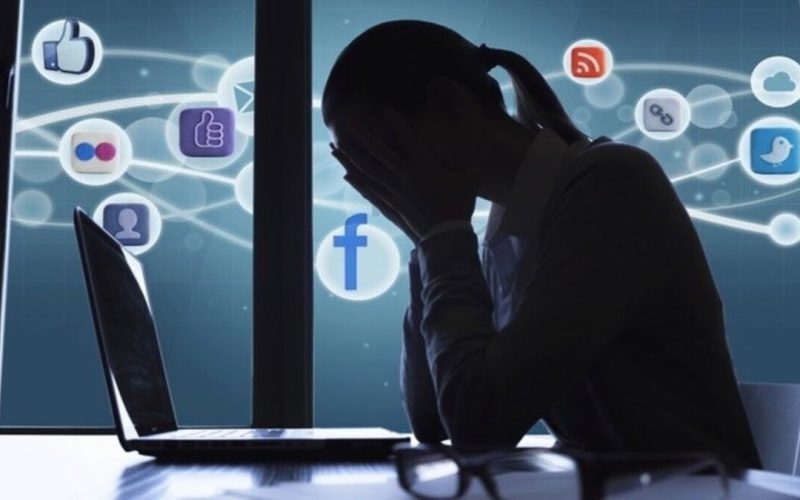
In the digital age, social media has become an integral part of our daily lives, offering unprecedented connectivity and access to information. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok have revolutionized communication, enabling users to share experiences, ideas, and moments with a global audience. However, the pervasive use of social media has sparked significant debate among researchers, mental health professionals, and the general public about its impact on mental health. This article delves into the latest studies to explore how social media influences mental well-being.
The Dual Nature of Social Media
Social media is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it provides a platform for social interaction, community building, and self-expression. On the other hand, it can contribute to feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression. Understanding this dual nature is crucial for comprehending its overall impact on mental health.
Positive Aspects of Social Media
- Social Connectivity: One of the most significant benefits of social media is its ability to connect people. For individuals who feel isolated due to geographical, social, or physical barriers, social media offers a lifeline. Studies have shown that maintaining social connections can improve mental health by providing emotional support and reducing feelings of loneliness.
- Access to Information and Resources: Social media platforms are valuable sources of information, offering users access to mental health resources, support groups, and educational content. For example, mental health organizations often use social media to disseminate information about coping strategies, treatment options, and mental health awareness campaigns.
- Self-Expression and Identity Formation: Social media allows individuals to express themselves and explore their identities. For many, this can be a therapeutic outlet for creativity and self-discovery. Research indicates that self-expression on social media can enhance self-esteem and foster a sense of belonging.
Negative Aspects of Social Media
- Comparison and Envy: One of the most cited negative effects of social media is the tendency for users to compare themselves to others. This phenomenon, often referred to as “social comparison,” can lead to feelings of inadequacy, envy, and low self-esteem. Studies have found that individuals who frequently compare themselves to others on social media are more likely to experience depressive symptoms.
- Cyberbullying and Harassment: The anonymity provided by social media can sometimes lead to negative behaviors such as cyberbullying and harassment. Victims of online bullying are at a higher risk of developing mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation. Research indicates that cyberbullying can have long-lasting psychological effects, particularly among adolescents.
- Addiction and Time Displacement: Excessive use of social media can lead to addiction, characterized by compulsive checking and posting. This behavior can displace time that could be spent on more fulfilling activities, such as face-to-face interactions, exercise, and hobbies. Studies have shown that social media addiction is associated with increased levels of stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.

What the Studies Show
Social Media and Depression
Several studies have explored the link between social media use and depression. A study published in the journal Depression and Anxiety found that individuals who spent more time on social media were more likely to report symptoms of depression. The study suggested that negative interactions, such as cyberbullying and social comparison, were significant contributors to these depressive symptoms.
Another study published in JAMA Psychiatry examined the impact of social media on adolescents. The researchers found that teens who spent more than three hours per day on social media were at a higher risk of developing mental health issues, including depression and anxiety. The study emphasized the importance of monitoring and moderating social media use among young people.
Social Media and Anxiety
Anxiety is another mental health condition that has been linked to social media use. A study published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior found that individuals who used multiple social media platforms were more likely to experience anxiety symptoms. The researchers suggested that the constant need to manage multiple online identities and the fear of missing out (FOMO) contributed to increased anxiety levels.
Additionally, a survey conducted by the Royal Society for Public Health in the UK found that social media platforms, particularly Instagram, were associated with higher levels of anxiety and poor body image among young people. The survey highlighted the role of photo-centric platforms in exacerbating anxiety related to appearance and self-worth.
Social Media and Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are another area of concern related to social media use. A study published in the journal Sleep Medicine found that excessive social media use, particularly before bedtime, was associated with poor sleep quality and insomnia. The researchers pointed to the stimulating nature of social media content and the blue light emitted by screens as factors that disrupt sleep patterns.
Furthermore, a study published in Preventive Medicine Reports found that individuals who used social media for more than two hours per day were more likely to report sleep disturbances. The study emphasized the importance of establishing healthy social media habits to promote better sleep hygiene.
Mitigating the Negative Impact
While the negative effects of social media on mental health are concerning, there are strategies that individuals can adopt to mitigate these impacts:
- Limit Screen Time: Setting boundaries on social media use can help reduce the risk of addiction and its associated mental health issues. Designating specific times for social media and taking regular breaks can promote a healthier balance.
- Curate Content: Being mindful of the content consumed on social media can make a significant difference. Unfollowing accounts that trigger negative emotions and following those that promote positivity and mental well-being can create a more supportive online environment.
- Engage in Offline Activities: Balancing online interactions with offline activities is crucial for mental health. Engaging in hobbies, physical exercise, and face-to-face social interactions can provide a sense of fulfillment and reduce the negative impact of social media.
- Seek Support: If social media use is causing significant distress, seeking support from mental health professionals can be beneficial. Therapists can provide coping strategies and help individuals develop healthier relationships with social media.
Conclusion
The impact of social media on mental health is a complex and multifaceted issue. While social media offers numerous benefits, including social connectivity, access to information, and self-expression, it also poses risks such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and addiction. The latest studies highlight the importance of understanding these dynamics and adopting strategies to mitigate the negative effects. By fostering a balanced and mindful approach to social media use, individuals can harness its positive potential while safeguarding their mental well-being.