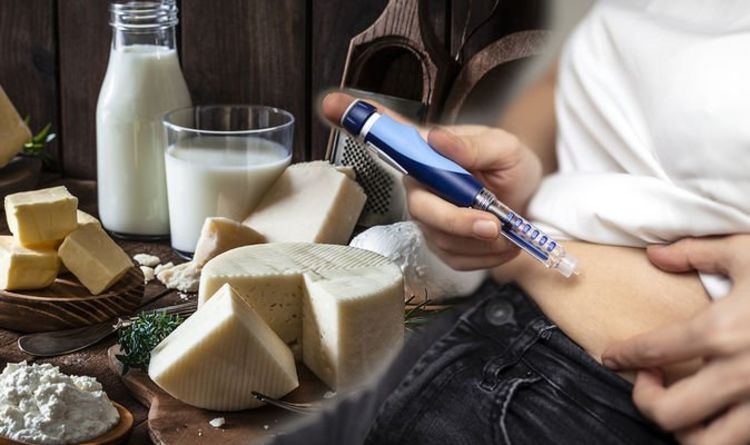
Understanding the impact of milk and dairy on blood sugar is crucial for individuals with diabetes. In this article, we’ll discuss how dairy products can affect blood sugar levels and provide guidance on selecting low-fat or unsweetened dairy options and dairy alternatives like almond or soy milk.
1. Milk and Blood Sugar:
Dairy and Carbohydrates:
Milk contains natural sugars, primarily in the form of lactose. These carbohydrates can affect blood sugar levels. It’s important to account for the carbohydrate content when planning your meals.

2. Low-Fat and Unsweetened Options:
Better Choices:
Opt for low-fat or unsweetened dairy products. These options provide protein and essential nutrients without the added sugars and fats often found in full-fat or flavored dairy.
3. Greek Yogurt:
Protein-Packed:
Greek yogurt is a protein-rich dairy choice. Opt for plain, unsweetened varieties, as they contain less sugar compared to flavored options.
4. Portion Control:
Balancing Carbohydrates:
Control portion sizes to manage carbohydrate intake. A standard serving of milk is typically one cup, containing about 12 grams of carbohydrates.
5. Dairy Alternatives:
Lactose-Free Options:
Dairy alternatives like almond or soy milk can be suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or those who prefer plant-based options. Choose unsweetened varieties to minimize sugar intake.
6. Sugar-Free Nut Milk:
Watch for Added Sugars:
When selecting almond or soy milk, check labels for added sugars. Opt for sugar-free options or those sweetened with non-caloric sweeteners like stevia.
7. Nutrient Content:
Fortified Alternatives:
Some dairy alternatives are fortified with essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D to match the nutritional value of dairy milk. Look for fortified options for a complete profile.
8. Nut Allergies:
Consider Allergies:
If you have nut allergies, choose soy, rice, oat, or hemp milk, among other dairy alternatives. Be cautious of cross-contamination with nut-based products.
9. Meal Pairing:
Balanced Choices:
Incorporate dairy or dairy alternatives into balanced meals. Pair them with fiber-rich foods like whole grains and vegetables to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
10. Individual Response:
Personalized Approach:
Blood sugar responses can vary among individuals. Monitor your own levels to understand how dairy or dairy alternatives affect you, allowing for personalized dietary adjustments.

Conclusion: Informed Selections
Milk and dairy alternatives can be part of a diabetes-friendly diet when selected mindfully. By choosing low-fat or unsweetened dairy products and monitoring portion sizes, you can enjoy the nutritional benefits of dairy without compromising blood sugar control. Additionally, dairy alternatives provide lactose-free and plant-based options for those with specific dietary preferences or needs.