How to Troubleshoot Network Adapter Problems in Windows
Network adapter issues can be frustrating and disruptive to your wired network connectivity. Slow connections, intermittent dropouts, and no connection at all can hinder productivity and cause inconvenience. To ensure stable network connectivity, it’s essential to know how to troubleshoot network adapter problems on your own.
Hardware Troubleshooting Steps for Network Adapter Issues:
Check Physical Connections:
Start by ensuring all network cables, optical cables, and network cards are securely and correctly seated in their respective ports or slots. If there are any loose or unplugged connections, reinsert the cables and adapters. If the network adapter still fails to connect, move on to the next step.
Verify LED Indicators:
Check the LED indicators on your network cards. If the link LEDs are not lighting up, it indicates a physical connection issue. Try inserting cables or adapters into different ports or slots to check for damaged ports. If the problem persists, consider replacing the cables or NIC cards to rule out any damage. Also, ensure that the cables and network devices connected to your adapter are compatible in terms of brand, data rate, and port type.
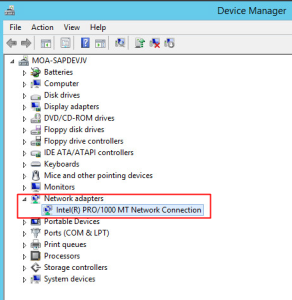
Check Network Adapter Status in Device Manager:
Use the Device Manager to confirm if your computer or server recognizes the network card. Follow these steps: a. Press Win+R on your keyboard to open the RUN box. b. Type “devmgmt.msc” and click OK to open Device Manager. c. Click Network Adapters to expand the section and double-click your network adapter entry. Check the network card status on the General tab. If it shows “This device is working properly,” the network card is functional. Otherwise, specific problems may exist with your card.
Check for Resource Conflicts in BIOS:
Verify whether there are resource conflicts between the network interface card (NIC) and other system components. Ideally, a NIC should not share an IRQ with SCSI or RAID controllers. You can adjust these settings within most server BIOS programs.
Verify Network Settings within the Operating System:
Ensure all protocols and network hardware (cables, hubs, switches, etc.) are correctly configured. All IP addresses should be unique, and DHCP should be set correctly to obtain a TCP/IP address automatically.
Ensure Proper Installation of TCP/IP Protocol:
Check if TCP/IP or other appropriate protocols are installed on your system: a. Right-click the My Network Places icon and select Properties. The network card should appear as Local Area Connection. b. Right-click the appropriate Local Area Connection and select Properties. Make sure that Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is installed. c. If TCP/IP is not installed, click Install, then Protocol, and select TCP/IP.
Verify the TCP/IP Address:
Open the command prompt and type “ipconfig” to check the IP address for your local machine. If it returns a 169.x.x.x or 0.0.0.0 address, try “ipconfig/release” followed by “ipconfig/renew” to obtain a proper TCP/IP address and Default Gateway address.
Ping the Loopback Address:
In the command prompt, type “ping 127.0.0.1” to send a message to the internal network stack on your machine. You should receive a response indicating the loopback address is functional.
Ping Your System’s IP Address:
Connect your system directly to another system or client using a crossover cable or dumb-hub. Set up TCP/IP using two consecutive addresses (e.g., 10.1.1.1 and 10.1.1.2) with the default subnet mask (255.0.0.0). From the command prompt, ping the client IP address. If you receive a response, the network adapter is working correctly.
Software Troubleshooting Steps for Network Adapter Issues:
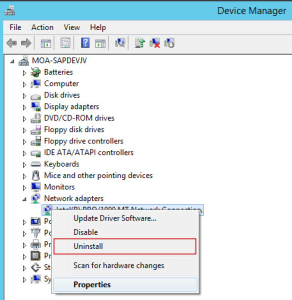
Reinstall Network Adapter Drivers: In Device Manager, right-click the network adapter name and select Uninstall. After confirming Device Uninstall, the driver will be rebooted and reinstalled.
Update Network Drivers:
Check the official website for network drivers for your product or seek assistance from customer support. Download and install the latest update for your network hardware if available.
Consider System Reinstallation or Updates:
If problems persist, consider reinstalling your Windows system or updating it to a newer version.
Need More Assistance?
If you’ve followed all the hardware and software troubleshooting steps and still face network adapter issues, it’s best to contact your network administrator or seek assistance from customer support. They can provide further guidance and solutions tailored to your specific setup.
Conclusion
Understanding how to troubleshoot network adapter problems in Windows can help you resolve common network connectivity issues efficiently. By identifying and resolving these issues, you can ensure a stable and seamless network experience for your devices.










