About the Author:
Hi everyone! I’m Sarah Jones, a registered nurse with over 15 years of experience working with geriatric patients. Witnessing the vulnerability of our elder population firsthand has fueled my passion for advocating for their well-being. Today, we’ll delve into a sensitive but crucial topic – elder abuse.
Understanding Elder Abuse
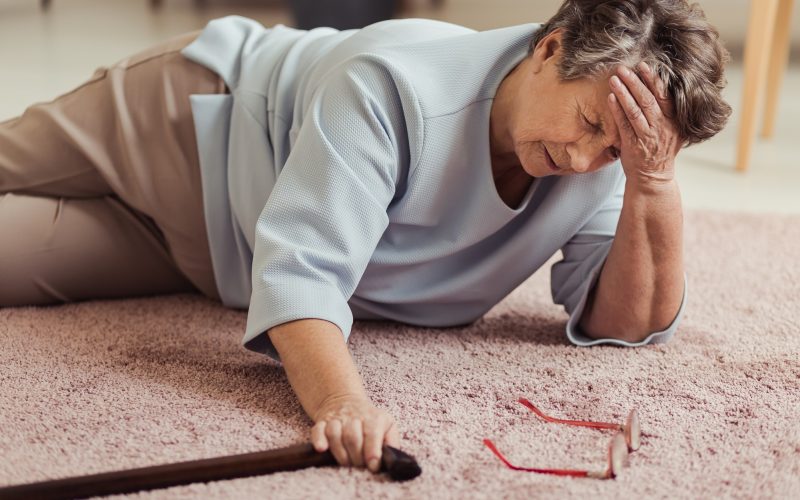
Elder abuse is the intentional infliction of physical, emotional, or financial harm on an older adult. It’s a shocking reality, affecting millions globally. According to the National Center on Elder Abuse ([National Center on Elder Abuse, ACL Administration for Community Living]), approximately 1 in 10 older adults experience abuse, neglect, or exploitation annually.
Types of Elder Abuse:
Here’s a breakdown of the different forms elder abuse can take:
- Physical Abuse: This includes hitting, shoving, or restraining an elder.
- Emotional Abuse: Yelling, threats, humiliation, and intimidation fall under this category.
- Financial Abuse: Exploiting an elder’s finances, stealing money or property, misusing power of attorney, or forcing them into unwanted financial transactions.
- Sexual Abuse: Any unwanted sexual contact or harassment.
- Neglect: Failing to provide basic needs like food, medication, hygiene, or shelter.
- Self-Neglect: When an elder refuses or is unable to care for themselves, leading to unsafe conditions.
Table 1: Recognizing the Signs of Elder Abuse
| Type of Abuse | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Physical Abuse | Bruises, cuts, broken bones, unexplained injuries, signs of restraint. |
| Emotional Abuse | Depression, anxiety, withdrawal, fear, changes in behavior. |
| Financial Abuse | Missing money or valuables, unexplained financial transactions, sudden changes in wills or power of attorney. |
| Sexual Abuse | Torn clothing, bleeding, bruises around genital areas, sexually transmitted infections. |
| Neglect | Dehydration, malnutrition, poor hygiene, unsanitary living conditions, medication errors. |
| Self-Neglect | Unkempt appearance, unmanaged medical conditions, unsafe living environment. |

Understanding the Risk Factors:
Several factors can increase an elder’s vulnerability to abuse:
- Isolation: Limited social contact or dependence on the abuser.
- Financial Dependence: Difficulty managing finances or relying on someone else.
- Physical or Cognitive Impairment: Conditions like dementia or declining physical health can make an elder more dependent.
- Substance Abuse: Addiction in the caregiver or elder can create a volatile environment.
Preventing Elder Abuse: You Can Make a Difference
While elder abuse is a serious concern, it’s preventable. Here’s how you can contribute to a safe and secure environment for your loved ones:
- Stay Connected: Regularly visit or call your aging parent. Engage in meaningful conversations and build trust.
- Empower Your Loved One: Encourage your parent to maintain some independence in decision-making and finances.
- Be Aware of the Signs: Keep an eye out for the signs and symptoms listed above.
- Talk About Finances: Discuss financial planning and consider appointing a trusted person to manage finances.
- Seek Help if Needed: If you suspect abuse, don’t hesitate to contact Adult Protective Services or a trusted professional.
Resources for Support
Here are some resources that offer help and support:
- National Center on Elder Abuse: [National Center on Elder Abuse, ACL Administration for Community Living] (1-800-677-1116)
- National Adult Protective Services Association (NAPSA)
- The Eldercare Locator
Remember, you are not alone. There are people who care about your loved one’s well-being, and there’s help available.
By working together, we can create a safe and supportive environment for our aging population.