Digital health platforms are reshaping the healthcare landscape, offering solutions that improve patient care through technology-driven innovations. By leveraging advanced tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), wearable devices, telemedicine, and mobile health (mHealth) applications, these platforms enhance the accessibility, personalization, and efficiency of healthcare delivery. This article explores the transformative impact of digital health platforms, backed by examples, case studies, and the undeniable benefits they bring to both patients and providers.
Key Areas of Impact
Digital health platforms have disrupted traditional healthcare practices, offering a range of benefits that impact both patients and healthcare providers. The key areas of transformation include telemedicine, remote monitoring, AI-driven healthcare solutions, and personalized health management. Let’s delve deeper into each of these areas.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring

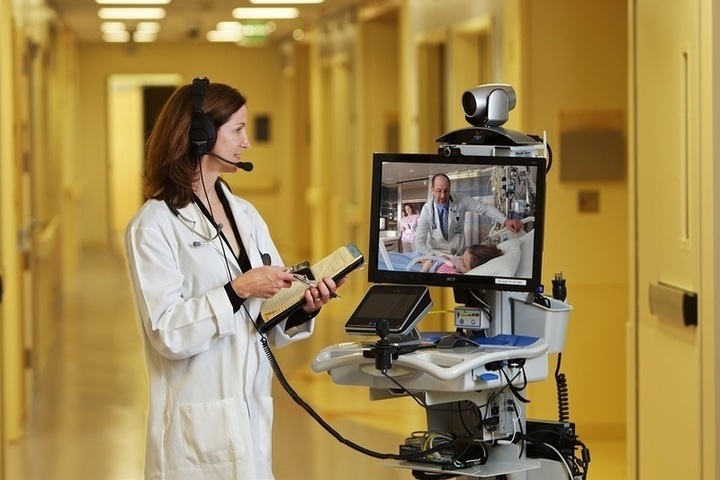
Telemedicine has gained significant traction, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, when physical consultations posed risks. Telemedicine allows patients to consult healthcare professionals from the comfort of their homes, breaking geographical barriers. For instance, rural and underserved populations now have access to specialists who were previously inaccessible.
Remote monitoring tools, such as wearable devices and smartphone applications, facilitate continuous tracking of vital signs and health metrics. Devices like the Apple Watch Series 10 and Garmin Fenix 7 Pro enable users to monitor their heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity in real time. These tools empower patients to take proactive roles in their health management.
Case Study: The use of remote monitoring devices in managing heart failure has shown promising results. Patients equipped with wearables that track their heart rate and oxygen levels reported fewer hospital visits and improved quality of life.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
AI is at the forefront of digital health innovation, offering solutions that optimize healthcare delivery. From predictive analytics to automated scheduling, AI-powered platforms streamline operations and enhance patient engagement.
For example, AI-driven appointment systems analyze patient profiles and external factors to optimize scheduling, significantly reducing no-shows. A recent trial in the UK reported a 30% reduction in missed appointments, saving healthcare providers substantial costs.
AI also aids in diagnostics and treatment planning. Algorithms analyze medical data to identify patterns that might be missed by human practitioners. This not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also accelerates the treatment process, benefiting patients with time-sensitive conditions.
Example: The AI system used by SkinVision helps detect early signs of skin cancer through a smartphone app, providing users with instant recommendations for seeking medical attention.
Innovative Health Devices
The rapid advancement in health technology has introduced groundbreaking devices that redefine patient care.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs):
- The Dexcom Stelo, an over-the-counter CGM, provides real-time glucose monitoring, allowing diabetes patients to manage their condition effectively.
- The Eversense 365, an implantable CGM approved by the FDA, lasts up to a year, reducing the need for frequent sensor replacements.
- Wearable Health Devices:
- The Apple Watch Series 10 detects sleep apnea by monitoring breathing patterns, providing early warnings.
- AirPods Pro 2 function as hearing aids for mild-to-moderate hearing loss, enabling users to conduct hearing tests and adjust settings through a simple app.
- Non-Invasive Monitoring Devices:
- The BioXensor uses radio frequency technology to measure blood glucose levels non-invasively.
- GlucoWear by Afon Technology integrates with smartwatches to provide real-time glucose monitoring without invasive procedures.
Case Study: A diabetes clinic in New York implemented Dexcom Stelo for its patients, reporting a 40% improvement in glucose level control and a 25% reduction in emergency visits.
Enhancements in Chronic Disease Management
Digital health platforms have proven particularly effective in managing chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart conditions. Mobile health (mHealth) applications play a vital role by offering personalized reminders, medication trackers, and telehealth consultations.
For instance, patients with diabetes benefit from continuous glucose monitors that track their blood sugar levels and provide instant feedback. Similarly, hypertension patients use devices that send daily readings to their doctors, allowing for real-time interventions.
Example: The mHealth platform MySugr provides diabetes patients with tools to log their meals, blood sugar levels, and activities. Studies have shown a 20% improvement in HbA1c levels among users after six months.
Patient Empowerment Through Wearable Devices

Wearable devices are no longer just fitness trackers; they are comprehensive health tools that empower users to monitor their health metrics and make informed decisions. Devices like the Oura Ring 4 offer detailed insights into sleep and recovery, while the Garmin Fenix 7 Pro caters to outdoor athletes with in-depth metrics and solar charging capabilities.
These tools not only encourage healthier lifestyles but also provide data that healthcare providers can use for better diagnostics and treatment planning.
Case Study: A corporate wellness program using Oura Rings reported a 15% increase in employee productivity, attributing the improvement to better sleep and recovery monitoring.
Challenges and Solutions in Digital Health
Despite the benefits, digital health platforms face challenges that need to be addressed for broader adoption:
- Data Privacy and Security:
- Ensuring the confidentiality of patient data is paramount. Strong encryption protocols and compliance with regulations like HIPAA are essential.
- Digital Divide:
- Access to digital health tools remains uneven, particularly in low-income and rural areas. Governments and organizations must invest in infrastructure and education to bridge this gap.
- System Integration:
- Seamless integration of digital health platforms with existing healthcare systems is crucial for maximizing their potential. Interoperable solutions and standardized data formats can facilitate this.
Future of Digital Health Platforms
The future of digital health looks promising, with emerging trends poised to further revolutionize patient care. Innovations such as virtual reality (VR) for pain management, blockchain for secure patient records, and AI for predictive analytics are just the beginning.
Example: VR platforms like AppliedVR are being used to manage chronic pain and anxiety, offering drug-free alternatives for patients.
Collaboration between tech companies and healthcare providers will play a crucial role in driving these advancements. By prioritizing user-centric designs and ethical considerations, digital health platforms can achieve their full potential.
Conclusion
Digital health platforms are undeniably transforming the healthcare industry, making it more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered. From telemedicine and AI-powered tools to innovative devices and mHealth applications, these technologies empower individuals to take charge of their health while enabling providers to deliver better care. As we address the challenges and embrace the opportunities, the future of healthcare will undoubtedly be brighter, healthier, and more inclusive for all.