The human immune system is an intricate network of cells, tissues, and organs that work in unison to defend the body against harmful pathogens. While genetics and lifestyle factors such as exercise and sleep play crucial roles in maintaining immune health, nutrition is a cornerstone that significantly influences immune function. This article delves into the relationship between nutrition and immune function, shedding light on how specific nutrients can bolster the body’s defense mechanisms.
The Immune System: A Brief Overview
Before exploring the impact of nutrition on immune function, it’s essential to understand the immune system’s structure and operation. The immune system comprises two primary components: the innate and adaptive immune responses. The innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense, offering immediate but non-specific protection against pathogens. In contrast, the adaptive immune response is slower but provides targeted and long-lasting immunity by recognizing and remembering specific pathogens.
Both components rely on a variety of cells, including white blood cells like lymphocytes and phagocytes, and signaling molecules like cytokines. Proper nutrition ensures that these cells and molecules function optimally, thereby enhancing the body’s ability to fend off infections and diseases.
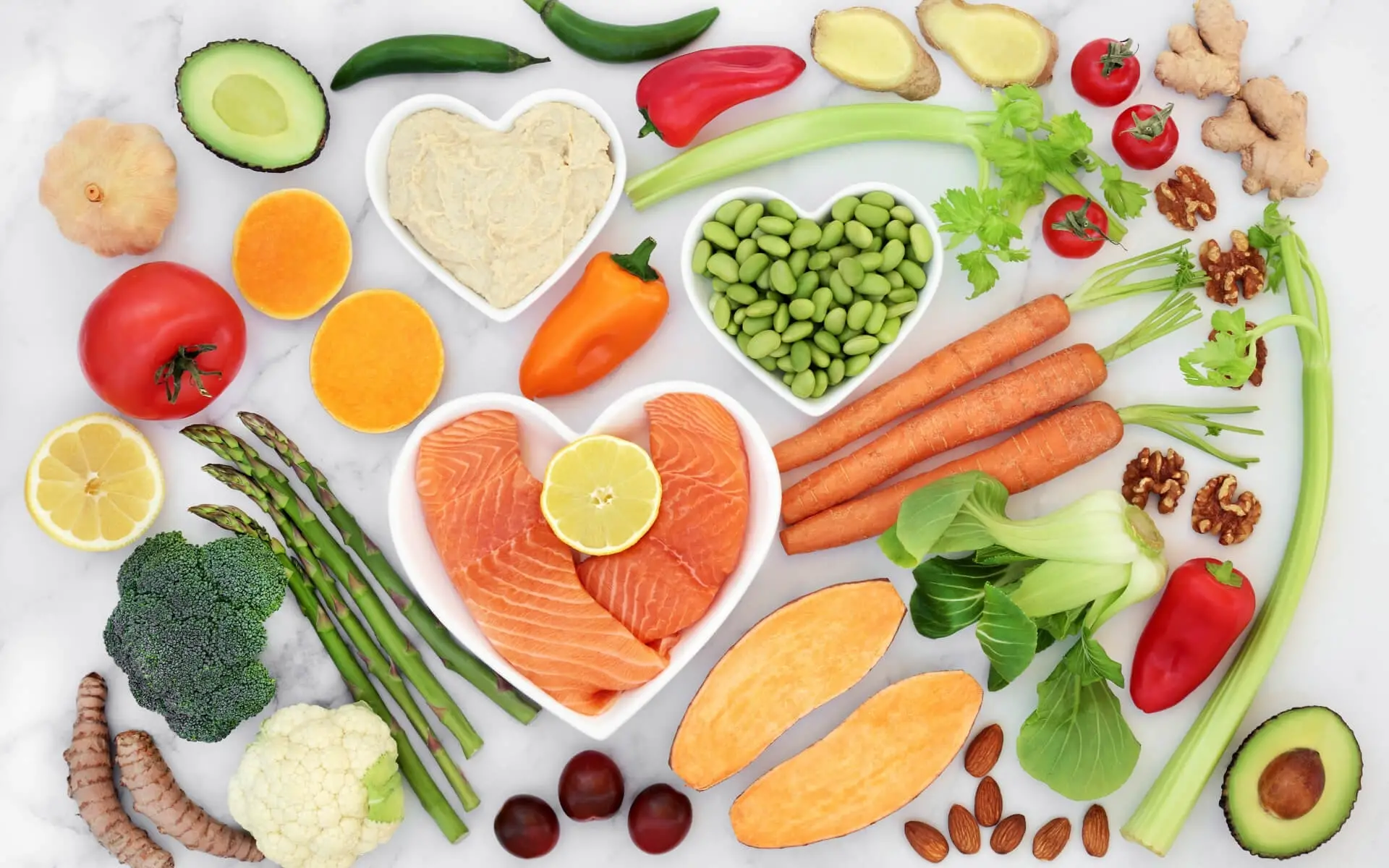
Key Nutrients That Enhance Immune Function
Vitamins
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, is perhaps the most well-known nutrient for immune support. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress caused by free radicals. Vitamin C also stimulates the production and function of white blood cells, particularly neutrophils, lymphocytes, and phagocytes, which are crucial for the innate immune response. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune response. It enhances the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages—white blood cells that are critical to the immune defense—and decreases inflammation. Sun exposure is a primary source of vitamin D, but it can also be obtained from foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is another potent antioxidant that helps combat oxidative stress. It enhances the function of T-cells, a type of lymphocyte involved in the adaptive immune response. Foods high in vitamin E include nuts, seeds, spinach, and broccoli.

Minerals
Zinc
Zinc is essential for the normal development and function of cells mediating innate immunity, such as neutrophils and natural killer cells. It also plays a role in the adaptive immune response by aiding in the development of T-cells and B-cells. Zinc deficiency can impair immune function, making the body more susceptible to infections. Good sources of zinc include meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds.
Selenium
Selenium is a trace element that acts as an antioxidant and supports the function of various immune cells. It aids in the production of cytokines, which are crucial for the immune response. Selenium-rich foods include Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains.
Proteins and Amino Acids
Proteins are the building blocks of the body’s cells and tissues, including those of the immune system. Amino acids, the components of proteins, are vital for the synthesis of immune cells and antibodies. Glutamine and arginine are two amino acids that have been shown to enhance immune function. Sources of high-quality protein include meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, and legumes.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have anti-inflammatory properties that can modulate the immune response. They influence the function of immune cells and the production of signaling molecules like cytokines. Fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
The gut microbiota plays a significant role in immune function. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health and, by extension, support the immune system. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish these beneficial bacteria. Together, they help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is crucial for a robust immune response. Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and fiber-rich foods like fruits and vegetables are good sources of probiotics and prebiotics.
The Impact of Malnutrition on Immune Function
Malnutrition, characterized by inadequate intake of essential nutrients, can severely impair immune function. It can lead to a reduction in the number and efficacy of immune cells, making the body more vulnerable to infections and diseases. Protein-energy malnutrition, for instance, can result in a weakened immune response, delayed wound healing, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Micronutrient deficiencies, such as lack of vitamins and minerals, can also compromise immune function. For example, vitamin A deficiency can impair the integrity of mucosal barriers, which are the body’s first line of defense against pathogens. Similarly, iron deficiency can affect the proliferation and activity of immune cells.
Dietary Recommendations for Optimal Immune Function
To maintain a robust immune system, it’s essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients. Here are some dietary recommendations to enhance immune function:
- Eat a Variety of Fruits and Vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support immune health.
- Include Lean Proteins: Foods like chicken, fish, beans, and tofu provide essential amino acids necessary for the production of immune cells.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids from sources like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts have anti-inflammatory properties that can modulate the immune response.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate fluid intake is essential for the optimal functioning of all bodily systems, including the immune system.
- Limit Processed Foods: High intake of processed foods can lead to inflammation and negatively impact immune function.
- Consider Probiotics and Prebiotics: Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fiber-rich fruits and vegetables can support a healthy gut microbiome, which is crucial for immune health.
Conclusion
Nutrition plays an indispensable role in enhancing immune function. A well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, proteins, and healthy fats can significantly bolster the body’s defense mechanisms. By understanding the impact of specific nutrients on the immune system, individuals can make informed dietary choices to support their overall health and well-being. As research continues to unveil the complex interactions between nutrition and immune function, it becomes increasingly clear that what we eat profoundly influences our ability to fight off infections and maintain optimal health.