Introduction
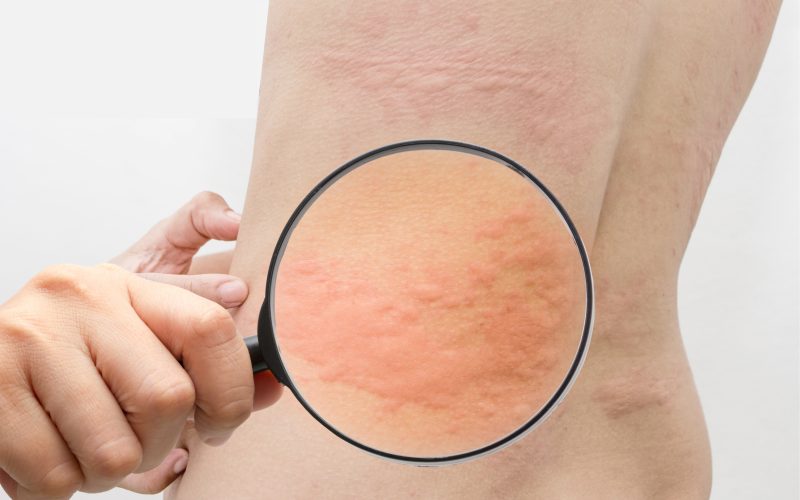
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. Understanding the triggers of shingles is crucial for preventing its occurrence and managing its symptoms effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various factors that can trigger shingles and explore strategies for minimizing the risk of developing this painful condition. Explore More About Other Health Issues And Their Solutions (Overcoming Addiction)
What is Shingles?
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the body’s nerve tissues. Years later, the virus may reactivate, leading to the development of shingles.
The primary symptom of shingles is a painful rash that typically appears as a single stripe of blisters on one side of the body. Other symptoms may include itching, burning sensations, fever, headache, and fatigue. While anyone who has had chickenpox can develop shingles, certain factors may increase the risk of its occurrence.
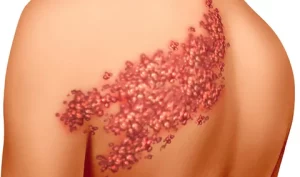
Factors That Trigger Shingles
1. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to shingles. Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy can compromise the immune system’s ability to keep the varicella-zoster virus in check, allowing it to reactivate and cause shingles.
2. Advanced Age
Age is a significant risk factor for shingles, with the likelihood of developing the condition increasing as one gets older. This is partly due to age-related changes in the immune system, which may make older adults more vulnerable to viral infections like shingles.
3. Stress
High levels of stress can weaken the immune system and trigger the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. Whether it’s emotional stress, physical stress from illness or injury, or chronic stress, managing stress levels is essential for reducing the risk of shingles.

4. Certain Medications
Some medications, such as corticosteroids and drugs used to suppress the immune system, may increase the risk of developing shingles. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional about the potential side effects of medications and strategies for minimizing the risk of shingles.
5. Trauma or Injury
Trauma or injury to the skin can sometimes trigger the onset of shingles. This may include burns, cuts, or other forms of skin damage that disrupt the body’s natural defense mechanisms and provide an opportunity for the varicella-zoster virus to reactivate.
Factors and Risk Levels
| Factor | Risk Level |
|---|---|
| Weakened Immune System | High |
| Advanced Age | Moderate to High |
| Stress | Moderate |
| Certain Medications | Moderate |
| Trauma or Injury | Low to Moderate |
Preventive Measures Against Shingles
While certain factors that trigger shingles may be beyond our control, there are steps individuals can take to reduce the risk of developing this painful condition.
1. Vaccination
The shingles vaccine is highly effective in preventing shingles and reducing the severity of symptoms in those who do develop the condition. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the shingles vaccine for adults aged 50 and older, even if they have previously had shingles.
2. Stress Management
Practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies can help lower stress levels and support overall immune function.
3. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, adequate sleep, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking, can bolster the immune system and reduce the risk of shingles.
4. Avoiding Close Contact with Infected Individuals
Since shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, avoiding close contact with individuals who have active shingles lesions can help prevent transmission of the virus and reduce the risk of infection.
5. Prompt Treatment of Skin Injuries
Promptly cleaning and treating any skin injuries or wounds can help prevent the varicella-zoster virus from entering the body through damaged skin and causing shingles.
Conclusion
Shingles can be a debilitating condition characterized by a painful rash and other distressing symptoms. By understanding the triggers of shingles and implementing preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this condition and minimize its impact on their health and well-being. From maintaining a healthy lifestyle to seeking vaccination, taking proactive steps is key to staying shingles-free.
For more information on shingles prevention and treatment, consult with a healthcare professional or visit reputable medical resources online.