Understanding Concussions
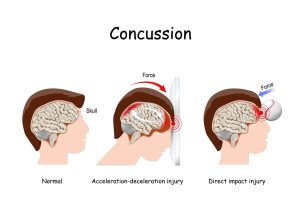
Concussions, often referred to as mild traumatic brain injuries (mTBIs), are commonly caused by a sudden blow or jolt to the head. While they are typically not life-threatening, they can have serious consequences if not properly identified and managed. Understanding the signs and symptoms of a concussion is crucial for prompt treatment and recovery. Explore your Health About (Warning Signs of Dangerous Health Conditions)
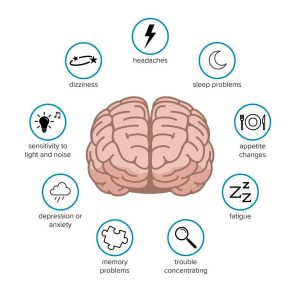
Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Physical Symptoms
- Headache: One of the most common symptoms of a concussion is a headache that may vary in intensity.
- Nausea or vomiting: Feeling nauseous or vomiting without any apparent cause could indicate a concussion.
- Dizziness or loss of balance: Difficulty maintaining balance or feeling dizzy can be indicative of a head injury.
- Sensitivity to light or noise: Increased sensitivity to light or noise is another common symptom.
Cognitive Symptoms
- Confusion or feeling foggy: Individuals with a concussion may experience confusion, difficulty concentrating, or feeling mentally foggy.
- Memory problems: Short-term memory loss or difficulty remembering recent events may occur.
- Slowed thinking: Cognitive processing may become slower than usual.
Emotional Symptoms
- Irritability: Sudden mood swings or irritability are common emotional symptoms of a concussion.
- Sadness or anxiety: Feelings of sadness, anxiety, or nervousness may also manifest.
- Depression: In some cases, a concussion can trigger or exacerbate symptoms of depression.
Sleep Disturbances
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep may occur following a concussion.
- Excessive sleepiness: Conversely, some individuals may experience excessive sleepiness or drowsiness.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you suspect that you or someone else has sustained a concussion, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. While some symptoms may appear immediately after the injury, others may develop hours or even days later. A healthcare professional can perform a thorough evaluation to assess the severity of the concussion and recommend appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Evaluation
During a medical evaluation for a concussion, the healthcare provider will conduct a comprehensive assessment, which may include:
- Physical examination: Checking for signs of head injury, such as bruising or swelling.
- Neurological assessment: Assessing cognitive function, balance, coordination, and reflexes.
- Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be ordered to rule out more severe brain injuries.
Treatment
The treatment for a concussion typically involves:
- Rest: Physical and cognitive rest is essential during the initial stages of recovery.
- Medication: Pain relievers may be prescribed to alleviate headaches.
- Monitoring: Close monitoring of symptoms is necessary to ensure proper healing.
- Gradual return to activity: Once symptoms improve, a gradual return to normal activities may be recommended.

Complications and Long-Term Effects
While most concussions resolve with time and rest, complications can arise, especially if the injury is not properly managed. Long-term effects of concussions may include:
- Post-concussion syndrome: Some individuals may experience persistent symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and difficulty concentrating for weeks or even months after the initial injury.
- Second impact syndrome: Sustaining a second concussion before the first one has fully healed can lead to more severe and potentially life-threatening complications.
- Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE): Repeated concussions or head trauma over time may increase the risk of developing CTE, a degenerative brain disease associated with cognitive and behavioral changes.
Preventing Concussions
While it may not be possible to prevent all concussions, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Wear protective gear: When engaging in sports or recreational activities that carry a risk of head injury, wearing appropriate protective gear such as helmets can help minimize the risk of concussion.
- Practice safe driving: Following traffic laws, wearing seat belts, and avoiding distractions while driving can reduce the risk of motor vehicle accidents and associated head injuries.
- Create safe environments: Taking measures to prevent falls in the home, such as installing handrails and using nonslip mats, can help prevent head injuries, especially in older adults.
Symptoms of Concussion vs. Post-Concussion Syndrome
| Symptom | Concussion | Post-Concussion Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | Yes | Yes |
| Nausea or vomiting | Yes | Yes |
| Dizziness | Yes | Yes |
| Memory problems | Yes | Yes |
| Irritability | Yes | Yes |
| Depression | Possible | Common |
| Insomnia | Possible | Common |
| Excessive sleepiness | Possible | Common |
Conclusion
Concussions are common yet potentially serious injuries that require prompt recognition and appropriate management. By understanding the signs and symptoms of a concussion, knowing when to seek medical attention, and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of sustaining a head injury and promote better outcomes for their overall health and well-being.