Introduction
In 2025, the world is becoming more connected than ever before, and the demand for faster, more reliable internet is increasing. As a result, two key technologies have emerged to address these needs: 5G and Wi-Fi 6. These technologies are designed to offer faster internet speeds, improved performance, and better connectivity. But with all the buzz around these two technologies, you may be wondering which one is better for your home network.
In this article, we will explore the differences between 5G and Wi-Fi 6, and help you determine which one is right for your home. We will compare their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks to help you make an informed decision for your internet needs.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile network technology. It is designed to replace 4G LTE networks, providing faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connections. 5G technology uses a combination of different frequencies, including higher-frequency millimeter waves, to deliver faster download and upload speeds, which is essential for supporting modern devices like smartphones, smart home gadgets, and even self-driving cars.
In a home setting, 5G can provide an alternative to traditional home broadband connections like fiber or cable. Many internet service providers (ISPs) are rolling out 5G home internet services that promise ultra-fast speeds and high reliability. However, 5G does come with some limitations, such as the availability of the network in certain areas and the need for compatible devices.
What is Wi-Fi 6?
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest standard in wireless networking technology. It is designed to improve upon Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) by providing faster speeds, greater capacity, and better efficiency. Wi-Fi 6 operates in the same frequency bands as its predecessors (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), but it uses more advanced technology to improve performance in crowded environments, like homes with many connected devices.
One of the key features of Wi-Fi 6 is OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access), which allows multiple devices to transmit data simultaneously, reducing delays and improving network efficiency. This makes Wi-Fi 6 ideal for households with many devices, like smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, and IoT devices.
Unlike 5G, Wi-Fi 6 doesn’t require a mobile network connection—it’s designed to work with your home router to provide wireless internet throughout your home. It’s especially useful for those who need reliable, high-speed internet for activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing.
5G vs. Wi-Fi 6: Key Differences
To help you understand which technology might be better for your home network, let’s break down the key differences between 5G and Wi-Fi 6.
1. Speed and Performance
5G offers incredibly fast download speeds that can reach up to 10 Gbps (depending on the network and location), which is much faster than 4G LTE. This makes 5G ideal for tasks like downloading large files, streaming 4K videos, and playing online games.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi 6 provides maximum speeds of around 9.6 Gbps, which is still faster than Wi-Fi 5, but it’s typically slower than 5G. However, Wi-Fi 6 excels in providing reliable connections to multiple devices in a crowded network environment, making it a better option for large homes or smart homes with numerous connected devices.
Tip: If speed is your top priority, 5G may be the better choice for your home. However, if you have many devices and need consistent performance, Wi-Fi 6 may be more suitable.
2. Coverage Area
5G offers impressive coverage over wide areas, but the signal strength can decrease as the frequency increases. While 5G can provide fast speeds over long distances, the millimeter waves (used for ultra-fast 5G) have limited range and can be blocked by obstacles like walls and buildings. As a result, 5G may not always be the best choice for homes located in areas with poor 5G coverage or for users who live in densely built environments.
Wi-Fi 6, on the other hand, is specifically designed to provide coverage within your home, using a router to distribute the signal across different rooms. The coverage area of Wi-Fi 6 is generally limited to your home, but it can cover large homes more efficiently thanks to the use of OFDMA technology.
Tip: If you’re looking for coverage across a large area, Wi-Fi 6 might be a more practical solution for your home, while 5G is better for urban or mobile use.
3. Device Capacity and Efficiency
One of the major advantages of Wi-Fi 6 is its ability to handle many devices at once. With Wi-Fi 6, multiple devices can transmit data simultaneously without overwhelming the network. This is particularly important for homes with many smart devices, such as smart thermostats, lights, security cameras, and other IoT gadgets.
In contrast, 5G has the potential to support a large number of devices as well, but its focus is more on providing fast speeds to individual devices, rather than managing multiple devices simultaneously.
Tip: If your home has many devices connected to the internet, Wi-Fi 6 will likely provide better efficiency and performance, especially in crowded environments.
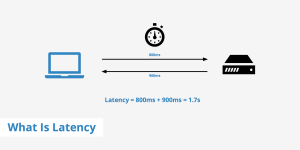
4. Latency
Latency refers to the delay in data transmission between devices. 5G offers extremely low latency, as low as 1 millisecond in ideal conditions. This makes 5G a great choice for real-time applications, like online gaming, video conferencing, and autonomous driving.
Wi-Fi 6 also provides low latency compared to Wi-Fi 5, but it’s generally not as low as 5G. However, the latency of Wi-Fi 6 is still suitable for most online activities like streaming, gaming, and browsing.
Tip: If you need super-low latency for activities like gaming or live streaming, 5G might offer the performance you need. For most everyday activities, Wi-Fi 6 will be more than enough.
5. Cost and Availability
5G can be more expensive than Wi-Fi 6 due to the infrastructure and the need for a 5G-capable phone or router. While 5G home internet is becoming more widely available, it may not be offered in all areas, and the cost of a 5G-enabled router or device could be higher than a standard Wi-Fi 6 router.
Wi-Fi 6, on the other hand, is typically less expensive and is widely available, with most modern routers supporting Wi-Fi 6 technology. If you’re already paying for a broadband internet service, upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 router can be a relatively affordable way to improve your home network.
Tip: If you’re looking for a cost-effective solution, Wi-Fi 6 may be a better choice. However, if you’re willing to invest in faster speeds and broader mobile coverage, 5G could be worth considering.
Table: 5G vs. Wi-Fi 6 – Key Differences
| Feature | 5G | Wi-Fi 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 10 Gbps (depending on network and location) | Up to 9.6 Gbps |
| Coverage Area | Wide, but may be limited by obstacles | Limited to your home or office space |
| Device Capacity | Supports many devices but focuses on individual speeds | Supports multiple devices simultaneously |
| Latency | As low as 1 millisecond | Low latency but not as low as 5G |
| Cost | Can be expensive depending on infrastructure | Typically less expensive and widely available |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are game-changers in the world of networking, each offering unique advantages depending on your needs. If you’re looking for ultra-fast speeds and low latency for real-time applications, 5G may be the better choice. However, if you have a lot of devices in your home and need efficient performance with stable coverage, Wi-Fi 6 will likely provide the best value.
As 5G and Wi-Fi 6 continue to evolve, these technologies will become even more integrated into our daily lives. By understanding the key differences and how each one fits into your home network, you can make an informed decision on which technology will work best for you.