Introduction
Pregnancy is a transformative experience for women, accompanied by various physiological changes. In some instances, these changes can impact blood sugar levels, leading to a condition known as gestational diabetes. Additionally, women with pre-existing diabetes require specialized care during pregnancy to ensure a healthy outcome for both the mother and the baby. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of diabetes and pregnancy, addressing key aspects and providing insights for expectant mothers.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly referred to as diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by elevated levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The two primary types are type 1 and type 2 diabetes. For a more in-depth understanding of each type, individuals are encouraged to explore the dedicated leaflets on Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes.
How Pregnancy Affects Diabetes
The intricate dance between pregnancy and diabetes involves an increased demand for insulin to regulate glucose levels in the body. This necessitates additional measures for women with diabetes during pregnancy. Optimal control is paramount, as poorly managed diabetes during pregnancy poses risks to both the mother and the developing baby. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and consultations with specialists become crucial elements in ensuring a safe and healthy pregnancy journey.
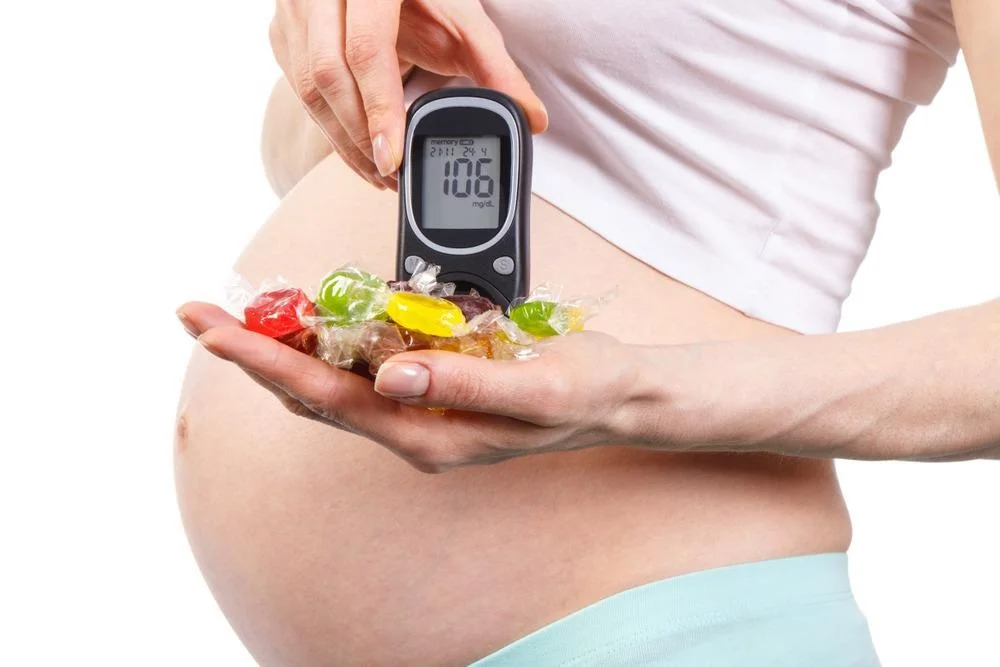
Gestational Diabetes: An Overview
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a unique form of diabetes that manifests for the first time during pregnancy. Research indicates that GDM occurs in approximately 1 in 20 to 1 in 50 pregnancies. While it typically resolves after childbirth, women diagnosed with GDM face risks similar to those with known diabetes, including potential complications during birth and an increased likelihood of requiring a caesarean section.
Understanding the risk factors for GDM is crucial, with age, weight, smoking, previous pregnancies, and family history playing significant roles.

Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of GDM often involves the glucose tolerance test (GTT). Once diagnosed, a comprehensive treatment plan is initiated. Lifestyle adjustments, encompassing dietary modifications and increased physical activity, are essential components. In some cases, medications such as metformin or insulin injections may be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels. Post-pregnancy, the discontinuation of insulin and other medications is a common practice.
Post-Pregnancy Recommendations for Women with GDM
Women with a history of GDM are encouraged to adopt a proactive approach to their health post-pregnancy. This includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excess weight gain, engaging in regular exercise, refraining from smoking, and attending regular check-ups to monitor blood sugar levels.
Advice for Women with Diabetes Before Pregnancy
Reducing risks for both mother and baby begins with careful pre-conception planning. Key recommendations include:
- Avoiding Unplanned Pregnancies: Contraception plays a crucial role in family planning.
- Optimal Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through dietary control and regular exercise.
- Regular Diabetes Check-ups: Periodic assessments for diabetes complications are imperative.
- Folic Acid Supplementation: Taking 5 mg of folic acid daily before and during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- Monitoring Ketones: Utilizing ketone testing strips if feeling unwell.
- Smoking Cessation: If applicable, quitting smoking is emphasized.
- Alcohol Moderation: Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake.

Risks of Diabetes During Pregnancy
Complications may arise during pregnancy, affecting both the mother and the baby. These complications include premature birth, an increased risk of miscarriage or stillbirth, higher birth weight, infections, and an elevated likelihood of requiring a caesarean section. The mother may face risks such as high blood pressure, blood clots, and potential exacerbation of long-term diabetes complications.
Treatment and Outlook
Frequent checks during pregnancy are essential, encompassing regular assessments of diabetes control and the baby’s well-being. Specialized care from healthcare professionals, including specialists, ensures that any potential issues are promptly addressed. The recommendation for women with diabetes to give birth in a hospital underscores the importance of immediate access to specialized care in case of complications.
Despite potential challenges, a positive outlook can be achieved through diligent monitoring, adherence to recommended treatments, and collaboration with healthcare providers. The ultimate goal is to ensure the well-being of both the mother and the baby throughout the pregnancy journey.
In conclusion
navigating diabetes during pregnancy requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition and a proactive approach to healthcare. Expectant mothers are encouraged to engage with healthcare professionals, follow guidelines diligently, and prioritize their well-being to optimize the chances of a healthy pregnancy and childbirth.