Introduction
A hiatal hernia is a condition where the upper part of the stomach protrudes into the chest through a small opening in the diaphragm, leading to symptoms like acid reflux. This guide delves into the various aspects of hiatal hernias, from their types to causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
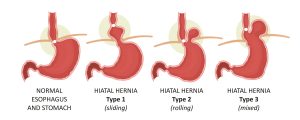
Types of Hiatal Hernias
- Sliding Hiatal Hernias (Type I):
- In this common type, the stomach intermittently slides up into the chest through the diaphragmatic opening.
- Paraesophageal Hernias (Type II-IV):
- These occur when a portion of the stomach pushes into the chest beside the esophagus, potentially causing more severe complications.
Causes of Hiatal Hernia
Understanding the factors that contribute to hiatal hernias is crucial:
- Birth Factors:
- Some individuals may be born with an unusually large hiatus, predisposing them to this condition.
- Injury or Trauma:
- Force from incidents like car accidents, where a seatbelt exerts pressure on the abdominal area, can lead to hiatal hernias.
- Obesity:
- Excess weight can increase the likelihood of developing a hiatal hernia.
- Pressure on Muscles:
- Chronic coughing, lifting heavy objects, repetitive vomiting, or straining during bowel movements can create persistent pressure on the surrounding muscles, contributing to hernia formation.
Diagnosing Hiatal Hernias
Identifying a hiatal hernia involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic techniques:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Healthcare providers inquire about symptoms such as acid reflux, belching, difficulty swallowing, and fatigue.
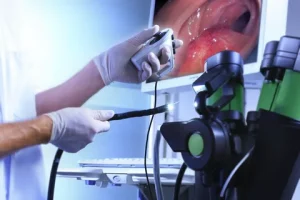
- Diagnostic Techniques:
-
- Barium X-ray or CT Scan:
- These imaging tests help visualize the location and positioning of gastric organs in the upper digestive tract.
- Endoscopy Exam:
- A thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is passed down the throat to inspect the esophagus and stomach for inflammation.
-
Symptoms of Hiatal Hernias
- Acid reflux
- Sour taste in the back of the mouth or throat
- Anemia
- Belching
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fatigue
- Heartburn
Treatments for Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal Hernia Lifestyle and Medication Treatments:
- Eating Habits Adjustments:
- Eating meals at least three to four hours before lying down.
- Consuming moderate to small portions of foods.
- Weight Management:
- Losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the stomach.
- Medications:
- Over-the-counter antacids or antihistamines.
- Prescription medications may be recommended by a healthcare professional to manage symptoms effectively.
- Sleeping Position:
- Sleeping in a slightly elevated position can alleviate symptoms.
- Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking is advised to improve overall health and reduce symptoms associated with hiatal hernias.
Surgical Treatments:
Surgery may be considered in cases where lifestyle changes and medications are insufficient to manage symptoms. The two main approaches are:
- Small Incision Surgery:
- This involves pulling the stomach down from the chest through small incisions, making the diaphragmatic opening smaller.
- Chest Repair:
- An alternative method where the hiatal hernia is repaired through the chest. Want to Know Other Health Problems And Their Treatments
Lifestyle vs. Surgical Treatments
| Treatment Type | Lifestyle Changes | Surgical Options |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Symptomatic relief | Permanent repair |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Involves small incisions or chest |
| Symptom Control | Management of symptoms | Targeted treatment of the hernia |
| Emergency Cases | Non-emergent | Emergency cases require immediate surgery |
Conclusion
In conclusion, gaining a thorough understanding of hiatal hernias empowers individuals to make informed decisions about managing this condition. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, medications, or surgical interventions, a tailored approach can be adopted based on individual needs and the severity of symptoms. Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those dealing with hiatal hernias.









