Introduction
Fatty liver, medically termed as hepatic steatosis, is a prevalent condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It is a growing concern worldwide, with significant implications for one’s health and well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and solutions to fatty liver is crucial for effective management and prevention of this condition.
What Causes Fatty Liver?
Fatty liver can be caused by various factors, including:
1. Poor Diet
Consumption of high-fat and high-calorie foods, particularly those rich in saturated fats and added sugars, can contribute to the development of fatty liver. Excessive intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and fried items overwhelms the liver’s capacity to metabolize fats efficiently, leading to fat accumulation.
2. Obesity
Obesity is closely linked to fatty liver disease. Excess body weight, especially abdominal obesity, increases the risk of developing fatty liver due to the increased deposition of fat in liver cells.
3. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a condition in which cells become less responsive to insulin, can promote fat accumulation in the liver. When cells resist insulin’s signal to take up glucose from the bloodstream, the liver compensates by producing more insulin, which can lead to increased fat synthesis.
4. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Chronic alcohol consumption is a leading cause of fatty liver disease. Alcohol is metabolized in the liver, and excessive intake can overwhelm its capacity, leading to fat accumulation and liver inflammation.
5. Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, tamoxifen, and antiretroviral drugs, can contribute to the development of fatty liver as a side effect of their usage.

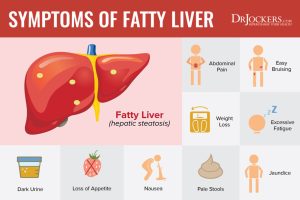
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it challenging to diagnose without medical evaluation. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience the following symptoms:
1. Fatigue
Persistent fatigue and weakness are common symptoms of fatty liver disease, often attributed to impaired liver function and energy metabolism.
2. Abdominal Discomfort
Some individuals with fatty liver may experience discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen, where the liver is located. This discomfort may be dull or sharp and can worsen after eating fatty or fried foods.
3. Enlarged Liver
As fat accumulates in the liver, it may become enlarged, leading to a feeling of fullness or pressure in the abdomen. In severe cases, the liver may be palpable below the ribcage.
4. Jaundice
In advanced stages of fatty liver disease, jaundice may occur due to impaired liver function, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes.
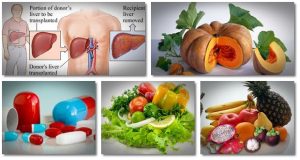
Solutions for Fatty Liver
1. Dietary Changes
Adopting a healthy, balanced diet is essential for managing fatty liver disease. Focus on consuming whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit intake of saturated fats, added sugars, and processed foods, and prioritize foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory nutrients.
2. Weight Loss
Losing excess weight through diet and exercise can significantly reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improve liver function. Aim for gradual, sustainable weight loss through a combination of calorie reduction and increased physical activity.
3. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity is beneficial for liver health and overall well-being. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Explore More About ( Link Between Diabetes or Fast Walking)
4. Limit Alcohol Consumption
If alcohol consumption is a contributing factor to liver disease, it’s essential to limit or abstain from alcohol entirely. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on individual health status and risk factors.
5. Medication Management
If liver disease is caused or exacerbated by certain medications, work with a healthcare provider to adjust dosage or explore alternative treatment options.
6. Regular Monitoring
Individuals diagnosed with liver disease should undergo regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider to assess liver function, track disease progression, and adjust treatment as needed.
Lifestyle Changes vs. Medical Interventions
| Lifestyle Changes | Medical Interventions |
|---|---|
| Dietary modifications: Limit saturated fats and added sugars, prioritize whole foods | Medication management: Adjust dosage or explore alternative treatments |
| Weight loss: Gradual, sustainable methods through diet and exercise | Regular monitoring: Assess liver function, track disease progression |
| Regular exercise: At least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity most days of the week | Surgical interventions: In severe cases, liver transplant may be necessary |
Conclusion
Fatty liver is a common yet potentially serious condition that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing lifestyle modifications and medical interventions as needed, individuals can effectively manage liver disease and reduce the risk of complications. Prioritizing a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption are key components of a comprehensive approach to liver management. With diligence and proper care, individuals can take control of their liver health and enjoy improved overall well-being.