Introduction: The Quest for Lunar Resources
As humanity continues to push the boundaries of space exploration, our celestial neighbor, the Moon, emerges as a promising destination for future ventures. Not only does the Moon spark our curiosity, but it also holds immense potential as a stepping stone for further space exploration, including eventual missions to Mars. One critical resource that has captured the attention of space agencies like NASA is water ice hidden beneath the lunar surface. In this article, we will delve into the strategic importance of water ice for future lunar ventures, exploring how this resource could revolutionize the way we approach lunar exploration.
Water Ice on the Moon: A Game Changer
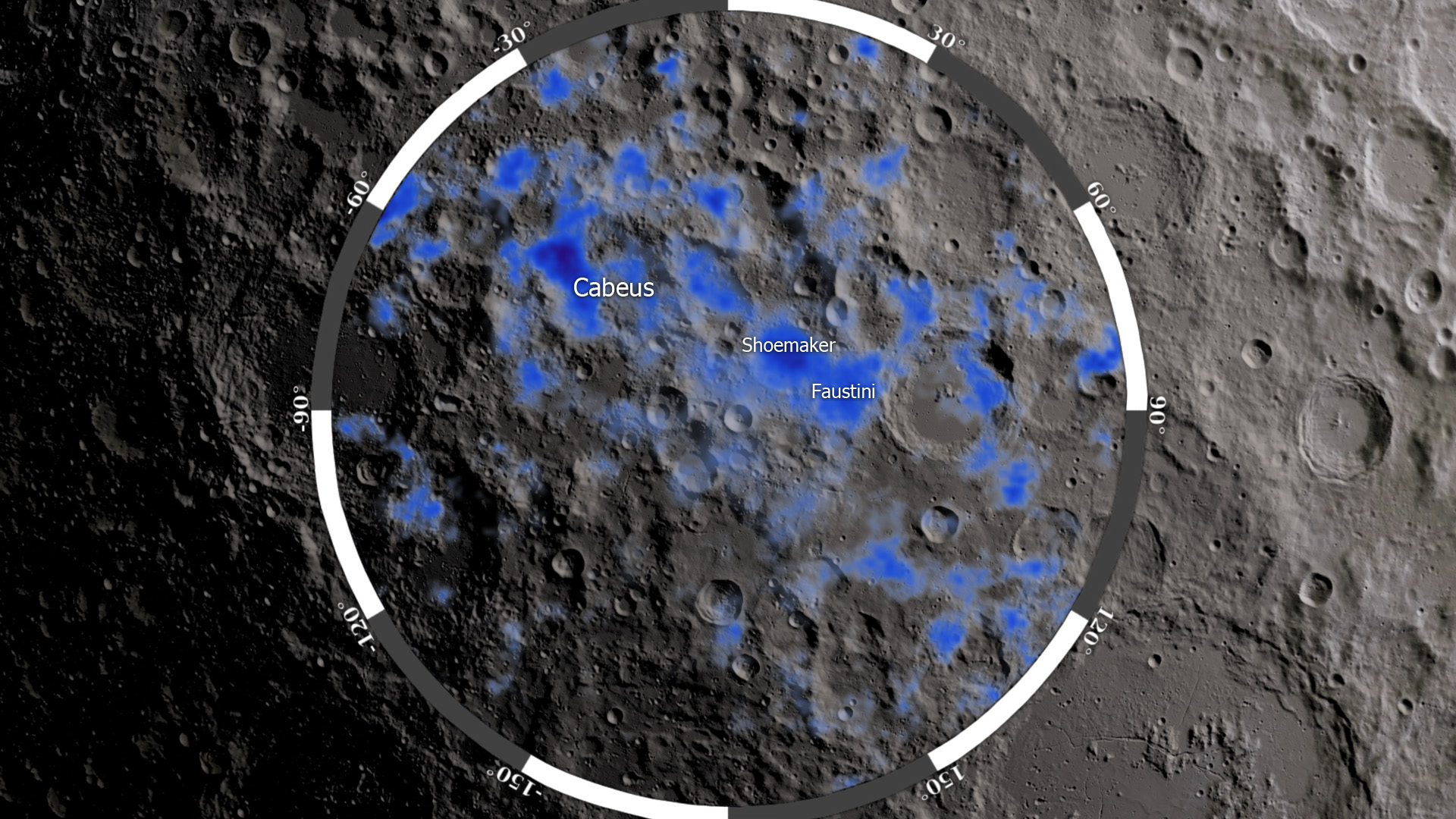
Water, an essential element for life as we know it, is a precious resource. The discovery of water ice on the Moon has opened up new possibilities for sustaining human life during extended lunar missions. The Moon’s poles, in particular, have been identified as regions with significant water ice deposits, providing a readily accessible source of this vital resource. Water ice is not only crucial for drinking and nourishment but can also be converted into oxygen for breathing and hydrogen for fuel.

NASA’s Vision: The Artemis Program
NASA’s Artemis program embodies the vision of returning humans to the Moon and establishing a sustainable presence. With a goal to land “the first woman and the next man” on the lunar surface by the mid-2020s, Artemis sets the stage for harnessing lunar resources like water ice. This program aims to utilize these resources to sustain human life and power further missions, laying the foundation for extended lunar stays and deep-space exploration.
The Strategic Importance of Water Ice
1. Life Sustenance:
Water is fundamental for human survival. Lunar water ice can sustain astronauts during extended lunar missions, reducing the need to transport water from Earth. This significantly lowers mission costs and enhances sustainability.
2. Fuel Production:
Water ice can be split into hydrogen and oxygen through a process called electrolysis. Hydrogen can be used as fuel, while oxygen provides breathable air. The ability to generate fuel from lunar resources is a game-changer, facilitating longer missions and enabling further exploration.
3. Shielding Against Radiation:
Water can act as an effective shield against radiation, a critical consideration for long-duration space missions. Lunar habitats could be partially constructed using water, enhancing radiation protection for astronauts.
4. Lunar Agriculture:
Water is pivotal for growing plants. Lunar water can potentially support agriculture, allowing the cultivation of crops for food production within lunar habitats, reducing dependence on Earth for supplies.
Harvesting Lunar Water Ice: Technological Advancements
The challenge lies in efficiently extracting and utilizing lunar water ice. Several technologies are being developed to achieve this:
- Regolith Excavation and Processing: Specialized machinery is being designed to excavate the lunar regolith, where water ice is embedded. Advanced processing techniques will then extract water from the regolith for further utilization.
- Prospecting and Mapping Technologies: Innovative technologies are under development to prospect and map the lunar surface, identifying regions with higher concentrations of water ice. This ensures targeted extraction for maximum efficiency.
- Drilling and Extracting Tools: Sophisticated drills and extracting tools are being engineered to bore into the lunar surface and extract water ice without contaminating the resource or the lunar environment.
Utilizing Lunar Water Ice: Fueling the Journey
The ability to convert water into hydrogen and oxygen offers a transformative potential for space travel:
- Lunar Lander Propulsion: Lunar landers can use hydrogen and oxygen derived from lunar water ice for propulsion, making landing and take-off more efficient and reducing the need for heavy fuel transport.
- Fuel for Deep Space Exploration: Hydrogen, obtained from water ice, can fuel spacecraft for missions beyond the Moon, such as trips to Mars or other planets within our solar system.
Lunar Habitats and Sustained Exploration
Lunar habitats are a vital component of sustainable lunar exploration. Water from lunar ice can be utilized in constructing these habitats and sustaining life within them. A combination of water-based shielding and controlled environmental systems powered by water-derived oxygen could ensure a safe and habitable space for astronauts.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the potential of lunar water ice is immense, challenges such as the development of efficient extraction technologies, creating self-sustaining habitats, and ensuring economic viability need to be addressed. International collaboration, continued research, and innovation will play a critical role in overcoming these hurdles.
Conclusion: Navigating the Lunar Seas of Potential
As we stand at the threshold of a new era in space exploration, water ice on the Moon emerges as a beacon of hope and possibility. The Artemis program by NASA exemplifies our commitment to sustainable lunar exploration, utilizing the abundant resources present on the Moon to fuel our journey beyond. As we navigate the lunar seas of potential, let us remain steadfast in our pursuit of knowledge and ingenuity, for the stars and beyond await our discovery.
Actionable Steps for Lunar Enthusiasts:
- Stay Informed and Engaged: Follow updates from NASA and reputable space news platforms to stay informed about the latest developments in lunar exploration.
- Advocate for Lunar Research: Support space agencies and initiatives aimed at lunar exploration. Encourage your peers and community to rally behind the vision of a sustainable lunar future.
- STEM Education and Careers: Encourage young individuals to pursue STEM education and careers, particularly in space sciences and engineering, to contribute to the future of lunar and space exploration.
- Explore Collaborations: Advocate for international collaborations in space exploration, emphasizing the collective responsibility of humanity in expanding our understanding of the universe