Introduction
Numbness and tingling sensations in the arms and legs can be alarming and uncomfortable. These sensations, often described as pins and needles, can occur due to various reasons ranging from temporary positions causing pressure on nerves to underlying medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes behind these sensations is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the possible reasons why your arms and legs may feel numb or tingly. All you Need to Know About Other Health Issues And Their Solutions (Natural Remedies For Constipation Relief)
Understanding Numbness and Tingling
Before exploring the potential causes, it’s important to grasp the nature of numbness and tingling. These sensations typically occur when there’s pressure on a nerve or when nerves are damaged. Numbness refers to a loss of sensation, while tingling involves a prickling or pins-and-needles sensation. These sensations can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as weakness or pain.

Common Causes of Numbness and Tingling
1. Poor Posture or Prolonged Pressure
One of the most common reasons for experiencing numbness or tingling in the arms and legs is prolonged pressure on nerves. Sitting or sleeping in awkward positions can compress nerves, leading to temporary numbness. This often resolves once the pressure is relieved.
2. Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage to the peripheral nerves, which can result from various factors such as diabetes, infections, or exposure to toxins. This condition commonly causes numbness, tingling, and pain, usually starting in the hands and feet and gradually spreading.
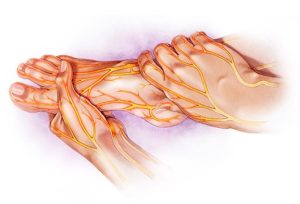
3. Pinched Nerves
A pinched nerve occurs when excessive pressure is applied to a nerve by surrounding tissues, such as bones, cartilage, muscles, or tendons. This can occur due to injury, repetitive motions, or conditions like herniated discs in the spine. Pinched nerves can lead to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area.
4. Circulation Problems
Poor circulation can also contribute to numbness and tingling in the arms and legs. Conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD) or Raynaud’s disease can impair blood flow to the extremities, leading to sensations of numbness, coldness, or tingling.
5. Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiencies in certain vitamins, particularly B vitamins like B12 and folate, can cause peripheral neuropathy and related symptoms. These vitamins play a crucial role in nerve function, and inadequate levels can lead to nerve damage and subsequent numbness or tingling.

6. Nerve Compression Syndromes
Various nerve compression syndromes, such as carpal tunnel syndrome in the wrists or cubital tunnel syndrome in the elbows, can result in numbness and tingling sensations. These conditions occur when nerves are compressed or irritated at specific points along their pathways.
7. Other Medical Conditions
Several other medical conditions may contribute to numbness and tingling in the arms and legs, including multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, hypothyroidism, and certain autoimmune disorders. These conditions often involve dysfunction of the nervous system, leading to sensory disturbances.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional numbness or tingling may not be cause for concern, persistent or recurrent symptoms warrant medical evaluation. Additionally, if numbness or tingling is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as weakness, loss of bladder or bowel control, or changes in coordination, it’s essential to seek prompt medical attention.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing the underlying cause of numbness and tingling typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and possibly additional tests such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography, blood tests, or imaging studies like MRI or CT scans. Treatment varies depending on the underlying cause but may include:
- Addressing underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies
- Physical therapy or occupational therapy to improve strength, flexibility, and posture
- Medications to manage pain, inflammation, or underlying conditions
- Splints or braces to alleviate pressure on nerves
- Lifestyle modifications such as ergonomic adjustments or exercise routines
Preventing Numbness and Tingling
While not all causes of numbness and tingling can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Maintain good posture, especially when sitting or sleeping
- Take frequent breaks to stretch and move if you have a sedentary lifestyle or perform repetitive tasks
- Avoid prolonged pressure on nerves by using ergonomic furniture or equipment
- Eat a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals
- Manage underlying health conditions such as diabetes or hypertension effectively
Common Causes of Numbness and Tingling
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Poor Posture or Prolonged Pressure | Sitting or sleeping in awkward positions leading to nerve compression. |
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Damage to peripheral nerves often associated with diabetes, infections, or exposure to toxins. |
| Pinched Nerves | Excessive pressure on nerves by surrounding tissues, commonly due to injury or herniated discs. |
| Circulation Problems | Impaired blood flow to the extremities, seen in conditions like peripheral artery disease or Raynaud’s disease. |
| Vitamin Deficiencies | Deficiencies in B vitamins such as B12 and folate, crucial for nerve function and integrity. |
| Nerve Compression Syndromes | Compression or irritation of nerves at specific points along their pathways, resulting in sensory disturbances. |
| Other Medical Conditions | Various conditions including multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, hypothyroidism, and autoimmune disorders. |
Conclusion
Numbness and tingling in the arms and legs can stem from various factors, ranging from temporary pressure on nerves to underlying medical conditions. Understanding the potential causes and seeking appropriate medical evaluation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management. By addressing the underlying cause and adopting preventive measures, you can alleviate symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
For personalized advice and treatment options, consult a healthcare professional. Don’t ignore persistent or concerning symptoms, as early intervention can lead to better outcomes and prevent complications.
Remember, your health and well-being are paramount. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize self-care.