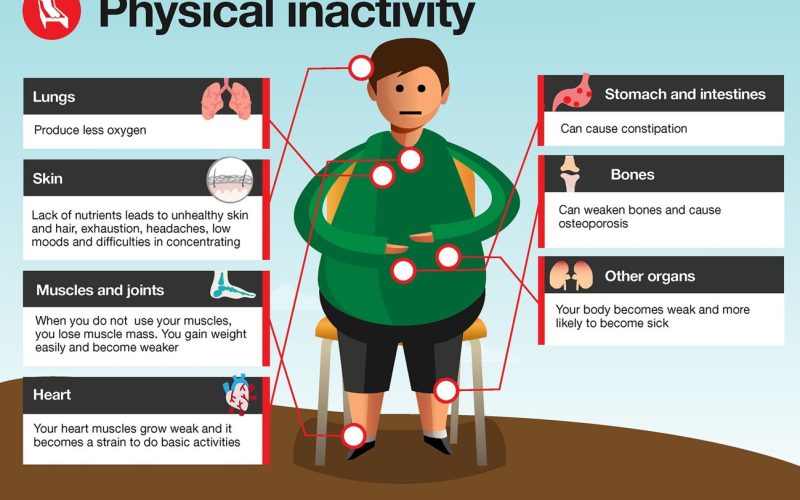
In journey towards a healthy heart and overall well-being, the impact of youth weight gain on long-term cardiovascular health cannot be overlooked. Recent research has shed light on the link between excess weight gain during youth and the risk of poor heart health later in. The patterns established in early years, including lifestyle habits, dietary choices, and physical activity levels, can significantly influence cardiovascular health outcomes in adulthood. Understanding the implications of youth weight gain on heart health is crucial for implementing preventive strategies, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, and mitigating the risk factors associated with poor heart health in later stages of life. Let’s delve into the correlation between youth weight gain and poor heart health and explore the implications for long-term cardiovascular well-being.
1. Early Weight Gain and Cardiovascular Risk:
The trajectory of weight gain during youth can serve as a critical determinant of cardiovascular risk factors in later years. Excessive weight gain in childhood or adolescence is associated with an increased likelihood of developing poor heart health markers such as high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, insulin resistance, and obesity. These risk factors, when established early in life, can set the stage for cardiovascular complications and chronic conditions in adulthood, underscoring the importance of addressing youth weight gain as a preventive measure for heart health.
2. Impact of Lifestyle Choices:
Youth weight gain is often intertwined with lifestyle choices that can influence heart health outcomes later in life. Sedentary behaviors, poor dietary habits, excess consumption of sugary or high-fat foods, and low levels of physical activity contribute to weight gain during youth and can perpetuate cardiovascular risk factors over time. Empowering young individuals to make healthy lifestyle choices, prioritize regular exercise, and adopt a balanced diet can help mitigate the impact of early weight gain on heart health.
3. Development of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome:
Excessive weight gain during youth can predispose individuals to obesity and metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, insulin resistance, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat. These components of metabolic syndrome are major contributors to poor heart health, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes, and coronary artery disease. Addressing weight gain and metabolic risk factors early on can help prevent the onset of chronic cardiovascular conditions in adulthood.

4. Long-Term Cardiovascular Consequences:
The implications of youth weight gain on heart health extend beyond immediate concerns, shaping the long-term cardiovascular consequences that individuals may face as they age. Unaddressed weight gain during youth can lead to persistent cardiovascular risk factors, accelerated atherosclerosis, impaired heart function, and an increased likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases in later stages of life. Recognizing the enduring impact of early weight gain on heart health underscores the importance of early intervention and lifestyle modifications to promote cardiovascular well-being throughout the lifespan.
5. Role of Prevention and Intervention:
Preventive strategies and interventions targeting youth weight gain are instrumental in safeguarding heart health and reducing the burden of cardiovascular diseases in adulthood. Early identification of individuals at risk of excessive weight gain, promotion of healthy eating habits, encouragement of physical activity, and fostering supportive environments that prioritize heart-healthy behaviors can help mitigate the detrimental effects of youth weight gain on cardiovascular wellness. By emphasizing prevention and intervention strategies, healthcare providers and communities can contribute to a healthier future for the next generation’s heart health.
6. Influence of Genetics and Environment:
The interplay of genetic predisposition and environmental factors plays a significant role in youth weight gain and its impact on heart health outcomes. Genetic variations that influence metabolism, fat storage, and appetite regulation can contribute to weight gain tendencies in youth, while environmental factors such as socioeconomic status, access to nutritious foods, cultural norms, and societal influences shape lifestyle choices that impact weight management and cardiovascular health. Understanding the complex interaction of genetics and environment can inform tailored approaches to address youth weight gain and support heart health promotion.
7. Importance of Early Education and Awareness:
Educating youth and families about the significance of maintaining a healthy weight, making nutritious food choices, and engaging in regular physical activity is paramount in promoting heart health from a young age. Early education and awareness initiatives that highlight the consequences of youth weight gain on cardiovascular well-being can empower individuals to take charge of their health, cultivate heart-healthy habits, and make informed decisions that support long-term heart health and overall wellness.
8. Lifelong Commitment to Heart Health:
Recognizing the impact of youth weight gain on heart health underscores the importance of a lifelong commitment to cardiovascular wellness. Adopting sustainable lifestyle changes, engaging in regular cardiovascular exercise, monitoring and controlling weight fluctuations, and seeking regular health screenings are essential components of maintaining heart health throughout the lifespan. By prioritizing heart-healthy behaviors and cultivating a proactive approach to cardiovascular well-being, individuals can mitigate the negative consequences of early weight gain and promote a healthier heart for years to come.
9. Collaborative Efforts for Heart Health Promotion:
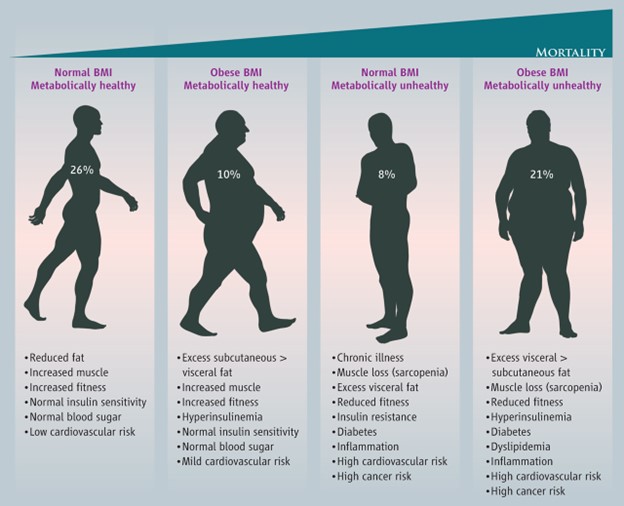
Addressing the association between youth weight gain and poor heart health requires collaborative efforts from healthcare professionals, educators, policymakers, families, and communities. By working together to create supportive environments, implement policies that promote healthy behaviors, increase access to nutritious foods, and raise awareness about the impact of weight gain on heart health, stakeholders can foster a culture of cardiovascular wellness and enhance the heart health outcomes of individuals across all age groups.
10. Empowering Future Generations:
Empowering future generations to prioritize heart health, make informed lifestyle choices, and take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy weight is essential for cultivating a society that values cardiovascular wellness. By instilling a culture of heart-healthy behaviors, promoting early intervention strategies, and fostering environments that nurture physical and emotional well-being, we can set the stage for a healthier, heart-conscious generation that is equipped to proactively manage their heart health and thrive throughout their lives.
Conclusion:
The connection between youth weight gain and poor heart health later in life highlights the critical importance of early intervention, preventive measures, and lifestyle modifications to safeguard cardiovascular wellness across the lifespan. Recognizing the implications of youth weight gain on heart health underscores the need for comprehensive strategies that address the root causes of excessive weight gain, promote heart-healthy behaviors, and empower individuals to prioritize their cardiovascular well-being from a young age. By emphasizing education, awareness, prevention, and intervention, we can pave the way for a healthier future generation with resilient hearts and thriving overall health.