Diabetes, a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, has long been a focal point of medical research and innovation. With the global prevalence of diabetes on the rise, the need for effective diabetes management strategies has never been more critical. Recent advancements in medical science have ushered in a new era of innovative treatments, offering hope for better control and improved quality of life for those living with diabetes. This article delves into these cutting-edge developments, exploring how they are transforming diabetes management.
Understanding Diabetes
Before delving into the latest treatments, it’s essential to understand the basics of diabetes. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. It primarily comes in two forms: Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type usually manifests in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 Diabetes: More common and typically develops in adults, though increasing numbers of children are being diagnosed. It is often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Effective diabetes management focuses on maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range to prevent complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure.
The Evolution of Diabetes Management
Traditionally, diabetes management has relied on a combination of lifestyle modifications, blood glucose monitoring, and medications, including insulin therapy for Type 1 diabetes and oral hypoglycemic agents for Type 2 diabetes. However, recent advancements have expanded the arsenal of tools available to patients and healthcare providers.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
One of the most significant breakthroughs in diabetes management is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM). Unlike traditional fingerstick tests that provide a snapshot of blood glucose levels, CGM systems continuously monitor glucose levels throughout the day and night. These devices use a small sensor inserted under the skin to measure interstitial glucose levels, providing real-time data and trends.
CGM offers several advantages:
- Improved Glycemic Control: Continuous data allows for better decision-making regarding insulin dosing, diet, and exercise.
- Hypoglycemia Prevention: CGM systems can alert users to impending low blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of severe hypoglycemic events.
- Personalized Insights: The data collected helps healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to individual needs.
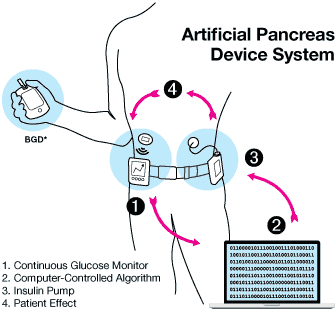
Artificial Pancreas Systems
Building on the foundation of CGM, artificial pancreas systems represent a significant leap forward in diabetes management. These systems combine CGM with insulin pumps and sophisticated algorithms to automate insulin delivery. The goal is to mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, adjusting insulin levels in real-time based on glucose readings.
The benefits of artificial pancreas systems include:
- Tighter Glycemic Control: Automated insulin delivery reduces the burden of constant monitoring and manual adjustments, leading to more stable blood glucose levels.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Improved control can lower the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Patients experience less stress and anxiety related to diabetes management.
SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Pharmacological advancements have also played a crucial role in diabetes management. Two classes of drugs, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, have garnered attention for their efficacy and additional health benefits.
- SGLT2 Inhibitors: These drugs work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose, leading to its excretion in the urine. Beyond lowering blood sugar levels, SGLT2 inhibitors have shown promise in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events and slowing the progression of kidney disease in diabetic patients.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These medications mimic the action of the GLP-1 hormone, which stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits glucagon release, and slows gastric emptying. They not only help control blood sugar but also promote weight loss and have cardiovascular benefits.
Gene Therapy and Regenerative Medicine
The field of gene therapy and regenerative medicine holds immense potential for diabetes management, particularly for Type 1 diabetes. Researchers are exploring ways to restore insulin production by either protecting existing beta cells or generating new ones.
- Beta Cell Regeneration: Scientists are investigating methods to stimulate the regeneration of beta cells within the pancreas. This approach aims to restore the body’s natural insulin production.
- Gene Editing: Technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 offer the possibility of correcting genetic defects that lead to Type 1 diabetes, potentially providing a cure for the condition.
Personalized Medicine
As our understanding of diabetes deepens, the concept of personalized medicine is gaining traction. Personalized medicine tailors treatment plans to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. This approach can optimize diabetes management by identifying the most effective interventions for each patient.
Digital Health and Telemedicine
The digital revolution has brought forth a plethora of tools and platforms that facilitate diabetes management. Mobile apps, wearable devices, and telemedicine services empower patients to take control of their health.
- Mobile Apps: Diabetes management apps help users track their blood glucose levels, medication, diet, and physical activity. They provide insights and reminders to stay on track.
- Wearable Devices: Fitness trackers and smartwatches equipped with health-monitoring features can assist in managing diabetes by tracking physical activity, heart rate, and even glucose levels.
- Telemedicine: Remote consultations with healthcare providers have become more accessible, allowing for regular check-ins and adjustments to treatment plans without the need for in-person visits.
Conclusion
The landscape of diabetes management is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and groundbreaking research. Continuous Glucose Monitoring, artificial pancreas systems, novel medications, gene therapy, personalized medicine, and digital health tools are transforming the way diabetes is managed. These innovations offer hope for improved glycemic control, reduced complications, and enhanced quality of life for individuals living with diabetes.
As we move forward, it is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and researchers to stay informed about these developments and collaborate to harness their full potential. With continued progress, the future of diabetes management looks promising, offering new possibilities for better health and well-being.