Introduction
In the realm of medical emergencies, sepsis stands out as a life-threatening condition that demands swift and decisive intervention. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate aspects of sepsis, from its definition and stages to the nuanced symptoms, causes, diagnostic approaches, and the crucial management strategies employed in its treatment.
Understanding Sepsis
Sepsis Unveiled
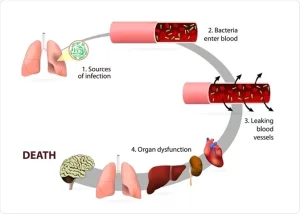
Sepsis is not merely an infection; it represents an intense and often devastating reaction of the body to an infection. The immune system, in its attempt to combat the invading pathogen, may inadvertently turn against normal tissues and organs, giving rise to widespread inflammation. Concurrently, an aberrant clotting response can result in the formation of blood clots, impeding blood flow and causing significant damage, including organ failure.
Evolving Stages
Traditionally categorized into three stages—sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock—healthcare providers now approach sepsis on a more fluid scale. This continuum spans from infection and bacteremia to full-blown sepsis and septic shock, with the potential for dysfunction in multiple organs, a phenomenon that may culminate in death if not promptly addressed.
Vulnerable Populations
While sepsis does not discriminate, certain groups face a heightened risk. Individuals grappling with infections, particularly bacteremia, find themselves particularly susceptible. Additionally, the elderly, newborns, pregnant individuals, those with underlying medical conditions like diabetes or kidney disease, individuals with weakened immune systems, and those undergoing hospitalization for unrelated medical reasons are more prone to the clutches of sepsis.
Symptoms and Causes
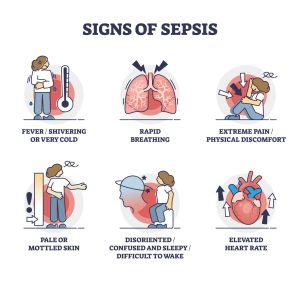
The Spectrum of Symptoms
Sepsis is a chameleon, manifesting with a diverse array of symptoms that can affect various bodily systems. Recognizing these symptoms is critical, as sepsis demands immediate medical attention. From the telltale sepsis rash and urinary issues to manifestations like low energy, fast heart rate, low blood pressure, fever, shaking, confusion, hyperventilation, and extreme pain—each symptom is a red flag signaling the urgency of intervention.
Unraveling the Causes
Bacterial infections take center stage as the most common culprits behind sepsis, but it’s crucial to acknowledge that fungal, parasitic, and viral infections can also propel the body into a septic state. Infections may originate in diverse anatomical sites, spanning the respiratory, urinary, gastrointestinal, central nervous, and integumentary systems.
Diagnosis and Tests
The Diagnostic Odyssey
Swift identification of infections with the potential to evolve into sepsis is paramount. Providers navigate this diagnostic odyssey by employing a multifaceted approach, encompassing physical examinations, laboratory tests, X-rays, and the utilization of tools like the quick sequential organ failure assessment (qSOFA). The criteria for diagnosing sepsis include parameters such as low blood pressure, elevated respiratory rate, and a low Glasgow coma scale score.
Diagnostic Arsenal
The diagnostic arsenal is comprehensive, involving an array of tests to pinpoint infections and assess organ damage. Blood tests, blood oxygen level evaluations, urine tests, and imaging procedures such as X-rays or CT scans collectively contribute to the diagnostic landscape.
Management and Treatment
The Urgency of Treatment
Once a diagnosis of sepsis is confirmed, the urgency of treatment cannot be overstated. Patients find themselves swiftly placed in the intensive care unit (ICU) for specialized care tailored to counteract the cascading effects of sepsis.
Multifaceted Treatment Approach
- Antibiotics: Deployed to combat bacterial infections.
- IV Fluids: Essential for maintaining adequate blood flow and preventing precipitous drops in blood pressure.
- Vasopressor Medications: Employed to tighten blood vessels and achieve a desirable blood pressure.
- Supportive Care: Addressing organ failures necessitates interventions like dialysis for kidney failure or mechanical ventilation for respiratory distress.
- Surgery: In instances of severe damage, surgical intervention may be warranted to remove compromised tissue.
Prevention
A Call for Vigilance
In the absence of strict diagnostic criteria for sepsis, early identification of individuals prone to developing the condition becomes paramount. Vigilance, particularly in high-risk populations, emerges as a cornerstone in preventing the complications associated with sepsis.
Conclusion
In the labyrinthine landscape of sepsis, understanding its intricacies, recognizing symptoms, and ensuring prompt and targeted treatment emerge as indispensable. This comprehensive exploration serves as a roadmap for healthcare providers, patients, and the general public alike, fostering awareness and paving the way for improved outcomes in the face of this formidable medical emergency.